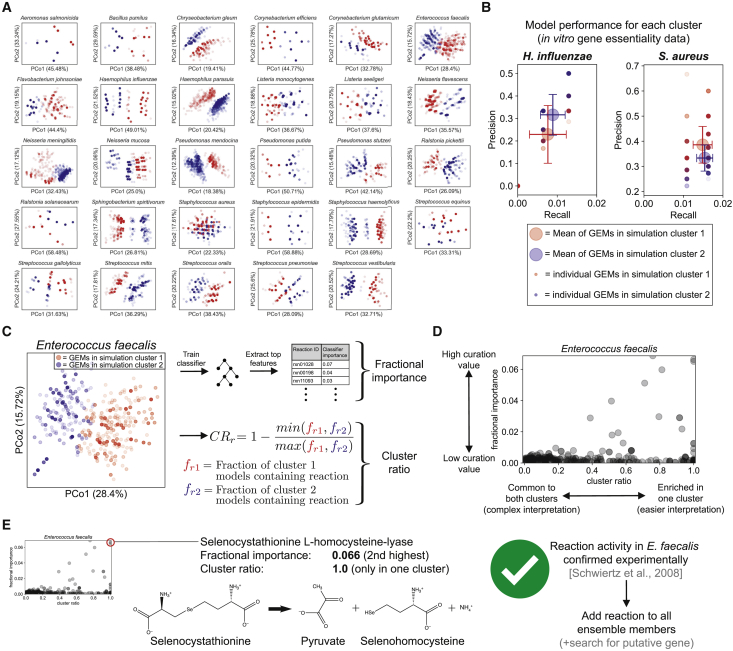
Figure 3.
Application of AMMEDEUS to Bacterial Species
(A) Ensemble gene essentiality simulations and unsupervised learning for all 29 species. Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) plots show the similarity between gene essentiality simulation profiles for each ensemble member. Within each PCoA plot, each point represents an ensemble member, colored by cluster membership as determined with k-means clustering (k = 2). PCoA is used solely for visualization; only k-means clustering results are used in AMMEDEUS. Percent variance in the pairwise distance matrix explained by each principal coordinate is indicated in parentheses.
(B) Evaluation of performance of GEMs in each simulation cluster compared to genome-wide gene essentiality data. Essentiality datasets from in vitro experiments were collected for Haemophilus influenzae and Staphylococcus aureus. Precision (TP/[TP + FP], TP = true positives, FP = false positives), and recall (TP/[TP+FN], FN = false negatives) were calculated for each ensemble member for each species. Small red and blue circles indicate an individual ensemble member, colored by simulation cluster membership. Large red and blue circles indicate mean behavior for ensemble members from each cluster, and error bars of same color extend above and below the mean by one standard deviation.
(C) Extraction of curation metrics (fractional importance and cluster ratio) for each reaction after the unsupervised learning step.
(D) Example curation guidance plot for Enterococcus faecalis.
(E) Example of a network feature driving simulation cluster membership. The metabolic activity, selenocystathionine L-homocysteine-lyase, is known to be catalyzed promiscuously by the enzyme cysteine-S-conjugate beta-lyase, which acts on a variety of S- and Se-conjugates. We discovered that this activity has been experimentally verified in vitro for E. faecalis but is not incorporated in biochemical databases. Water is excluded from reactants for visualization.