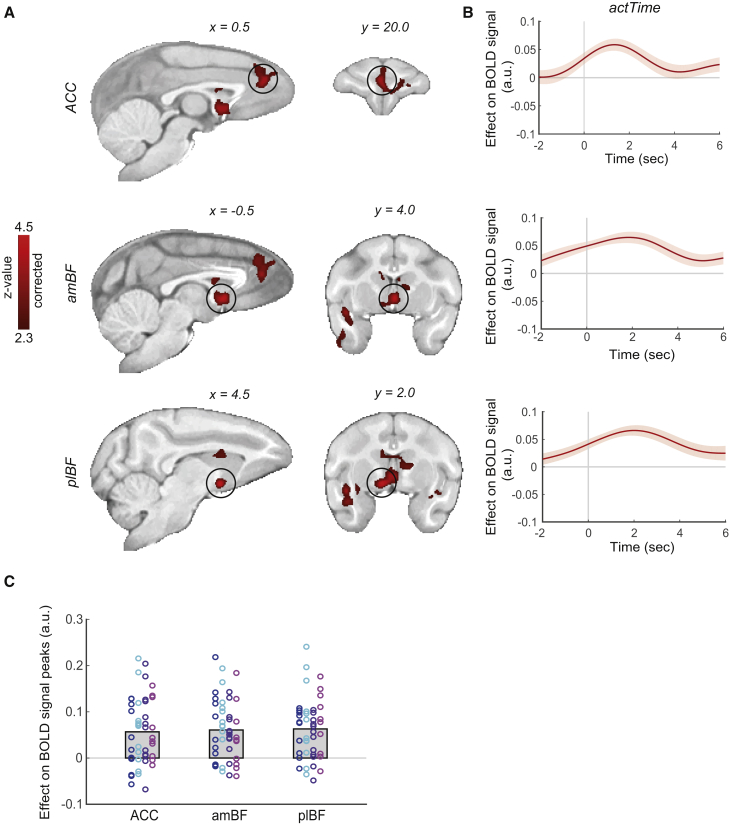
Figure 4.
The ACC and BF Encode Time to Act
(A) Whole-brain analysis showing voxels where activity reflected parametric variation in the empirically observed actTime. Here we focused on areas with bilateral/midline activity: the ACC (top panel) and BF (middle [amBF] and bottom [plBF] panels). Whole-brain cluster-based correction, Z > 2.3.
(B) ROI time course analysis of the ACC (top panel), amBF (middle panel), and plBF (bottom panel), showing the relationship between BOLD and actTime. The lines and shadings show the mean and standard error (SE) of the β weights across the sessions, respectively. Time zero is the response time. Note that, because of delay in the BOLD hemodynamic response function, the BOLD signal time course peaks 3 s after neural activity. When the delay in BOLD response is taken into account, it is clear that BOLD activity reflects neural events occurring before the response onset.
(C) No significant difference in actTime encoding was observed between the ACC, amBF, and plBF. Each color represents one animal, and each ring is the peak beta-weight of one testing session. The gray columns illustrate the group mean.
See also Figures S2 and S3 and Table S1.