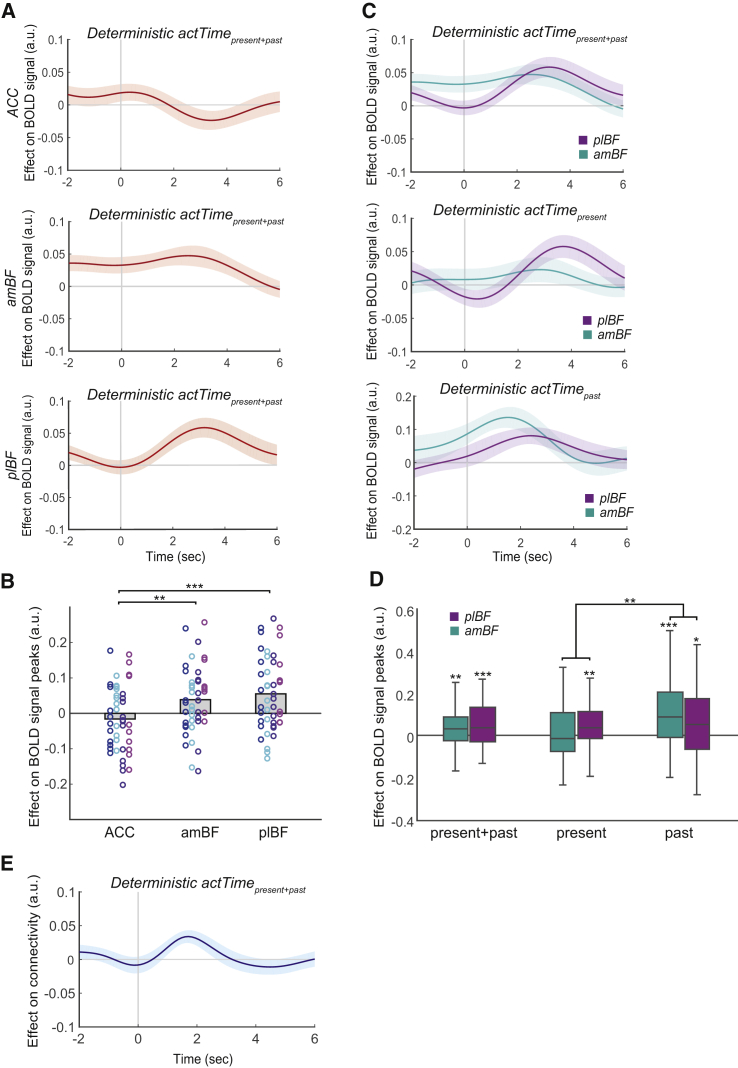
Figure 5.
The BF Encodes the Deterministic Component of Time to Act
(A) ROI time course analysis of the ACC, amBF, and plBF, showing the relationship between BOLD activity and deterministic actTime estimated from present and past context. Format is as in Figure 4B.
(B) The relationship between deterministic actTime and BOLD signal was significantly stronger in the plBF and amBF compared with the ACC. Format is as in Figure 4C.
(C) ROI time course analysis of the amBF and plBF, showing the relationship between BOLD activity and deterministic actTime as estimated from present and past, present, and past contextual factors.
(D) The relationship between deterministic actTime, as estimated from past contextual factors, and BOLD signal was significantly stronger in the amBF compared with the plBF. In boxplots, the central line indicates the median, and the bottom and top edges of the box indicate the 25th and 75th percentiles, respectively. Whiskers extend to the most extreme data points not considered outliers.
(E) PPI analysis between the BOLD signal in the plBF and amBF, with deterministic actTime as the psychological factor. Trial-by-trial variation in the activity in the plBF was significantly related to trial-by-trial variation in the activity in the amBF as a function of deterministic actTime.
One-sample t tests and multilevel ANOVA followed by pairwise t test. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. See also Figure S4.