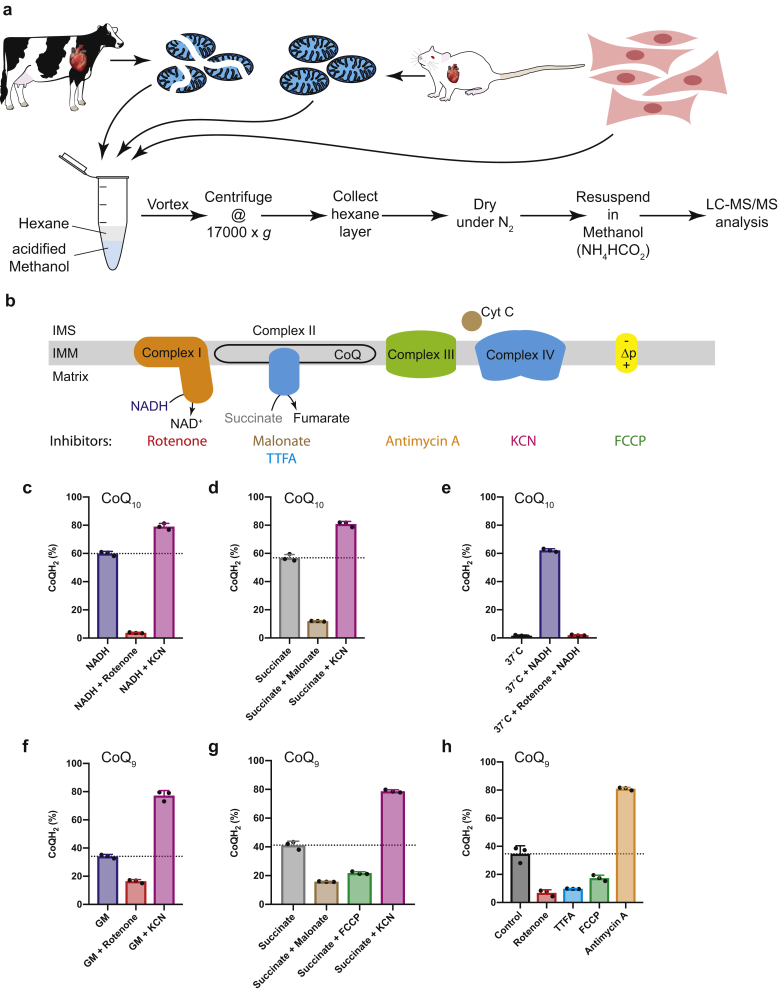
Fig. 5.
Extracting CoQ from biological samples and modifying the CoQ redox state in mitochondrial membranes, mitochondria and cells.
a A two-phase extraction with acidified methanol and hexane was used to extract CoQ from bovine mitochondrial membranes, mitochondria and cells. CoQ from incubations of biological samples was extracted by vortexing in extraction solution, phase separation by centrifugation and resuspending the extract in MS sample buffer (methanol with 2 mM ammonium formate). b Various inhibitors can be used to manipulate the mitochondrial CoQ redox state in biological samples. c-h Bovine heart mitochondrial membranes (BHMM), rat heart mitochondria (RHM) and C2C12 cells were incubated in KPi (BHMM), KCl (RHM) buffer or DMEM (cells) and different combinations of substrates and inhibitors were added before CoQ extraction and LC-MS/MS analysis of the CoQ redox state. All incubations were performed for 5 min at 37°C except otherwise indicated. CoQ redox state of: c BHMM incubated with NADH or NADH combined with rotenone or KCN. d BHMM incubated with succinate or succinate combined with malonate or KCN. e BHMM incubated for 20 min at 37°C. NADH or rotenone + NADH was added to indicated samples after 15 min f RHM incubated with glutamate + malate (GM) or GM combined with rotenone or KCN. g RHM incubated with succinate or succinate combined with malonate, FCCP or KCN. h C2C12 cells incubated in standard DMEM with FCCP, rotenone, TTFA or Antimycin A. For all experiments, data are represented as mean ± S.D. of 3 replicates. The proportion of CoQH2 is shown for the indicated most prevalent CoQ species.