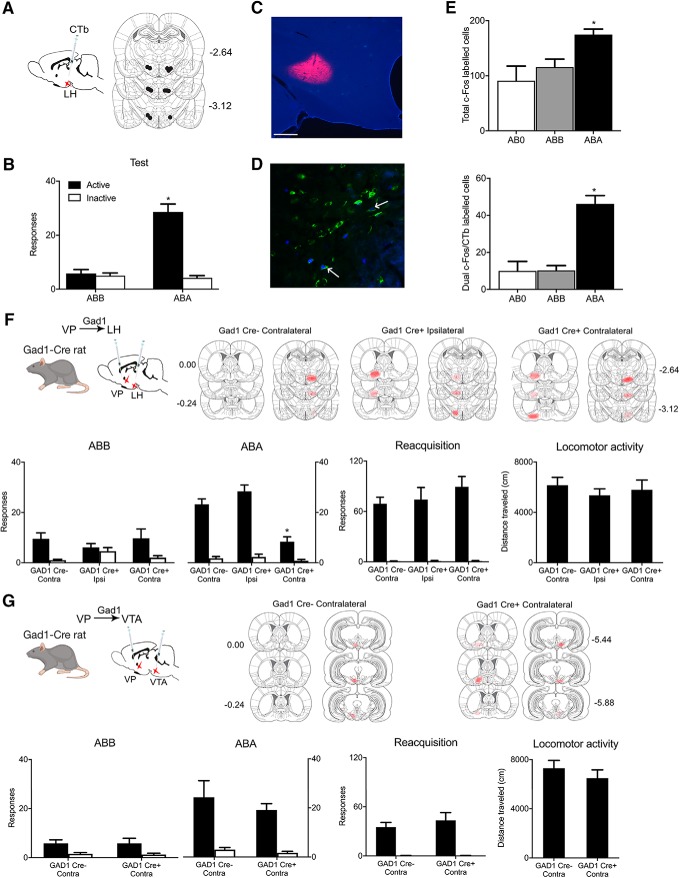
Figure 2.
VPGad1 neurons promote relapse via LH. A, C, CTb-488 or CTb-555 was applied to LH prior training and testing, Scale bar, 200 μm. B, ABA renewal of alcohol seeking. D, Example of c-Fos (blue), CTb (green), and dual labeling (shown by arrows) in VP. E, ABA renewal was associated with c-Fos expression in VP neurons including in VP→LH neurons. F, Cre-dependent inhibitory hM4Di was applied to VP of Gad1-Cre rats and hM4Di also applied to LH of the same animals. Locations of hM4Di expression shown for all animals at 10% opacity. Chemogenetic disconnection of VPGad1→LH pathway reduced renewal but not reacquisition or locomotor activity. G, Cre-dependent inhibitory hM4Di was applied to VP of Gad1-Cre rats and hM4Di also applied to VTA of the same animals. Locations of hM4Di expression shown for all animals at 10% opacity. Chemogenetic disconnection of VPGad1→VTA pathway had no effect on renewal, reacquisition, or locomotor activity. *p < 0.05.