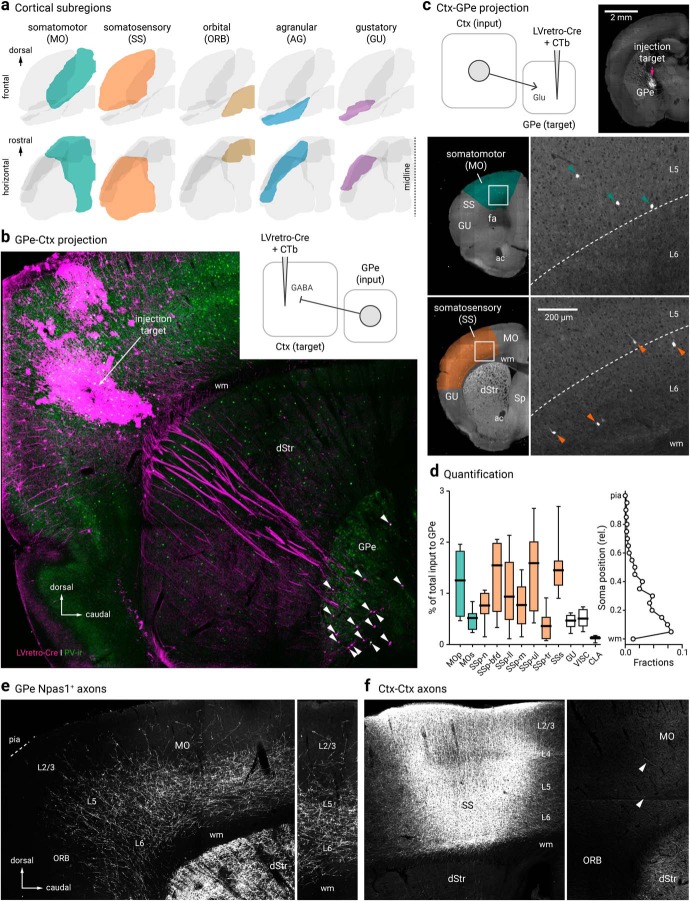
Figure 4.
Cortico-pallido-cortical macroscopic anatomy. a, Different cortical subregions examined in this study are highlighted. For clarity, frontal (top) and horizontal (bottom) views are shown. b, A confocal micrograph showing a representative example of retrogradely-labeled cortex-projecting GPe neurons (arrowhead) using LVretro-Cre in a LSL-tdTomato mouse; PV-immunolabeling (green) was performed in this example. Inset: experimental setup. LVretro-Cre and CTb were injected into different cortical areas mentioned in a, c, Top left, experimental setup: LVretro-Cre and CTb were injected into the GPe. Cortical inputs to the GPe were mapped using two-photon tomography. Top right, Two-photon image showing the location of the injection site. Bottom, representative two-photon images from coronal sections showing GPe-projecting cortical neurons were found primarily in layer 5 and 6 of MO and SS. d, Left, quantification of GPe-projecting neurons across the entire cortex. Medians, interquartile ranges, and 10th to 90th percentiles are represented in a graphical format. Right, laminar position of GPe-projecting neurons. e, Low-magnification image of Npas1+ pallido-cortical axons spanning across ORB, MO, and SS. Note the highest density occurred in layers 5 and 6 of MO followed by SS and dropped off precipitately rostrally in the ORB. Axons extend as far as layer 2/3. f, Local cortical infection in a Npas1-Cre-tdTom mouse confirmed axons visible in rostral cortical regions were from GPe projection and not ectopic infection of cortical neurons in the caudal areas. Injection site in SS (left) resulted in very low density of caudal to rostral cortico-cortical connectivity in MO and ORB (right). Arrowheads indicate the presence of cortical axons that arose from the more caudal regions. dStr, dorsal striatum; CLA, claustrum; MOp, primary somatomotor; MOs, secondary somatomotor; ORB, orbital; Sp, septum; SSp-n, primary somatosensory, nose; SSp-bfd, primary somatosensory, barrel field; SSp-ll, primary somatosensory, lower limb; SSp-m, primary somatosensory, mouth; SSp-ul, primary somatosensory, upper limb; SSp-tr, primary somatosensory, trunk; SSs, secondary somatosensory; VISC, visceral; ac, anterior commissure; fa, anterior forceps; wm, white matter.