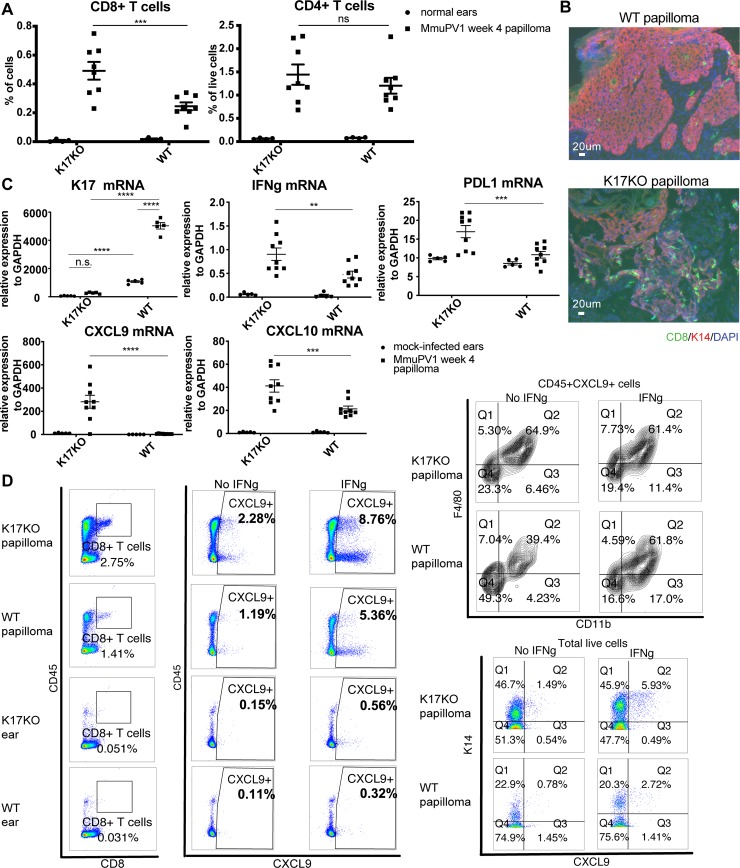
Fig 4. Lack of stress keratin 17 leads to increased infiltration of CD8+ T cells and increased expression of IFNg-related genes.
Mouse ears were infected with 109 VGE MmuPV1(Prep#1) per site. A) Percentage of CD8+ and CD4+ T cells based on flow cytometry analysis of normal ears (circles) versus ear MmuPv1 papillomas (squares) 4 weeks post-infection. For quantification of other populations, see S4A Fig. B) Immunofluorescent staining of frozen tissue sections of ear papillomas at 4 weeks post-infection. Green: CD8; Red: keratin 14 (K14); Blue: DAPI. Representative image for n = 4 samples (K17KO) and n = 6 samples (WT). C) RT-qPCR analysis of bulk RNA in mock-infected ears (circles) and ear MmuPV1 papillomas (squares) from K17KO and WT tissue 4 weeks post-infection. K17 expression was measured by TaqMan probe. IFNγ, PDL1, CXCL9 and CXCL10 were measured by SYBR Green method. GAPDH was used for normalization. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. 2-way ANOVA Sidak multiple comparison was used. **p<0.01; ***p<0.005; ****p<0.001; ns = not significant. D) Week 4 papilloma and uninfected normal ears were harvested from K17KO and WT FVB/N mice. Single cell suspension was cultured with or without recombinant mouse IFNγ (1000 U) in the presence of protein transport inhibitor for 16 hours. Cells were washed and stained with GhostDye to exclude dead cells, then stained with cell surface marker and intracellular CXCL9. A small aliquot of each sample was stained with K14 and CXCL9 only. (Left panel) Both CD45+ and CD45- cells could produce CXCL9 from papilloma tissues, with CD45- cells being the major population. (Top right panel) Within CD45+ CXCL9+ cells, majority of the cells were CD11b+F4/80+ macrophages. (Bottom right panel) Majority of the CXCL9-producing cells were stained K14+. Representative sample is shown for n = 3 K17KO papilloma and n = 3 WT papilloma. Only one K17KO ear and one WT ear were included as control.