Fig. 4. Behavior of microtubules that changed travel direction on patterned kinesins.
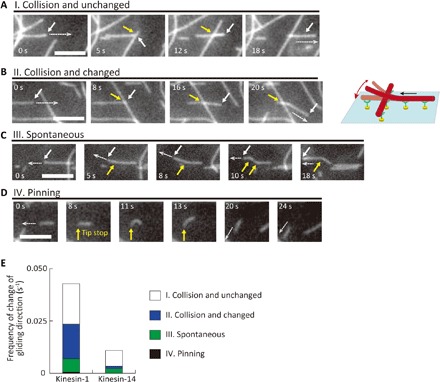
(A to D) Representative sequential images of the microtubules. Scale bars, 5 μm (A) “I. Collision and unchanged”: A microtubule did not change direction after collision; (B) “II. Collision and changed”: A microtubule changed direction after a collision. The white arrows indicate the leading tip of the microtubule. The white dashed arrows show the direction of microtubule gliding. The yellow arrows indicate the point of collision; (C) “III. Spontaneous”: A microtubule spontaneously changed its gliding direction. The yellow arrows indicate the position in which the leading tip changed its direction; (D) “IV. Pinning”: A microtubule changed direction because the leading end was pinned. (E) Frequency of the events (I) to (IV) on patterned kinesin-1 and kinesin-14.
