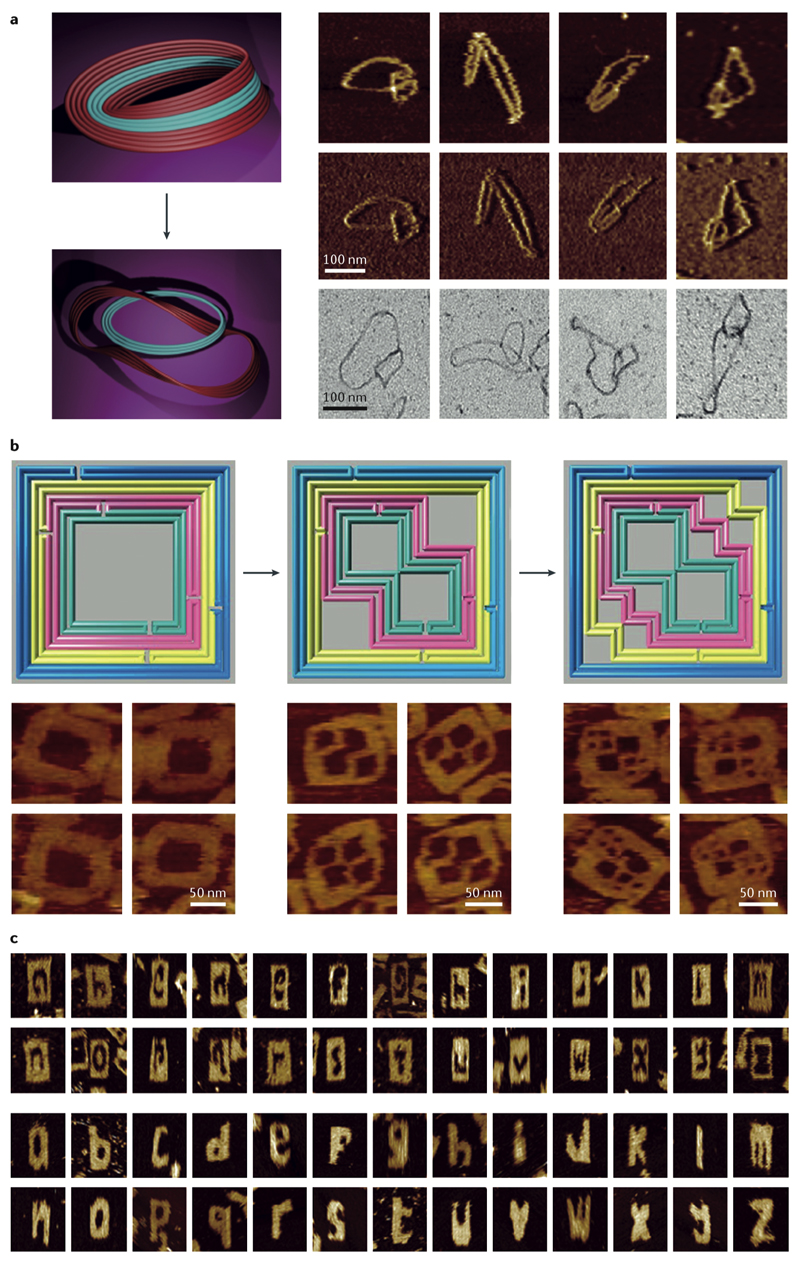
Fig. 4. Reshaping nanostructures using strand displacement reaction (SDR).
a| A DNA origami Möbius was cut along its strips using SDR to produce two interlocked rings (left). The atomic force microscopy (AFM) height (right, top row), amplitude (right, middle row), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) (right, lower row) images of the products83. b| The left origami frame was transformed to the middle and then the right frame using staple subset removal by SDR and addition of a new subset of staples as confirmed by the AFM (bottom row)84. c| AFM images of the SDR-mediated carved letters of alphabet off a 2D molecular canvas assembled using single-stranded DNA brick assembly technique85. Panels A-C were adapted from REFs. 83, 84, 85, respectively, with permissions from Springer Nature, American Chemical Society, Wiley-VCH Verlag.