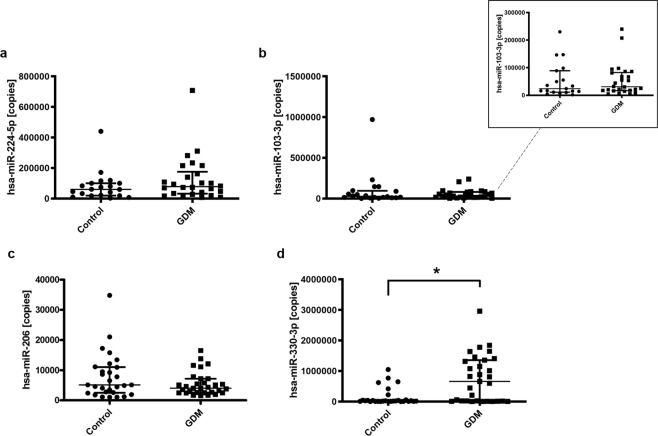
Figure 1.
Detection of diabetes-associated circulating serum miRNAs associated with glucose tolerance and homeostasis in the serum of patients with GDM and non-diabetic controls. (a), miR-224-5p levels were detectable in serum of control (median [IQR], 60298 [19595–100208] copies, n = 20) and gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) patients (median [IQR], 78205 [32239–175925] copies, n = 26). Significance determined by Mann–Whitney U test, p = 0.215. (b), miR-103-3p levels detected in serum of control (median [IQR], 28588 [11769–95796] copies, n = 20) and gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) patients (median [IQR], 30804 [16991–82426] copies, n = 26). Significance determined by Mann–Whitney U test, p = 0.763. (c), miR-206 levels were detected in serum of control (median [IQR], 5109 [2480–11028] copies, n = 29) and gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) patients (median [IQR], 4048 [2541–7195] copies, n = 31). Significance determined by Mann–Whitney U test, p = 0.420. (d), miR-330-3p levels detected in the serum of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) patients (median [IQR], 656943 [16149–1355000] copies, n = 31) were found to be significantly higher than those of nondiabetic controls (median [IQR], 20098 [8734–50016] copies, n = 29). Significance determined by Mann–Whitney U test, p = 0.003.