Figure 1.
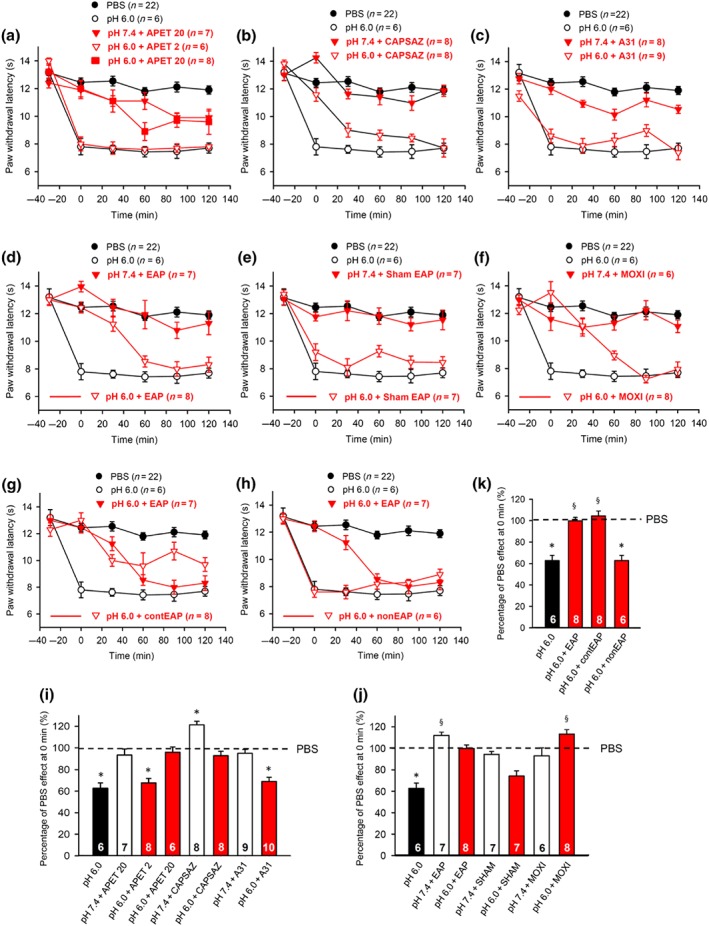
Modulation by pharmacological antagonists and acupuncture family procedures of acute thermal hypersensitivity caused by local acidification to pH 6.0. At −30 min, pH 7.4 or pH 6.0 PBS alone, APETx2 (20 μM), capsazepine (10 μM), or A‐317491 (300 nM), all dissolved in pH 7.4 or pH 6.0 PBS were injected to the left hind paw of rats; in another series of experiments, EAP or moxibustion, both for 30 min, was delivered to the Zusanli acupoint (ST36) of rats at the ipsilateral or contralateral side, again after injecting pH 7.4 or pH 6.0 PBS. For sham EAP, the needle was positioned as for EAP, but without electrical stimulation. The PWL was determined at −30 min and every 30 min afterwards, six times in total, until the 120‐min time point. This experimental protocol was used in Figures 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. One hundred and eleven rats were used to generate the data present in this figure (a–f). The time‐dependent effects of APETx2 (a), capsazepine (b), A‐317491 (c), EAP (d), sham acupuncture (e), moxibustion (f), contralateral EAP (g), and EAP at a non‐acupoint (h) are shown on the acidification‐induced decrease of PWL. For comparison, the change in PWL measured after injection of pH 7.4 PBS injection was plotted at each time point. Mean ± SEM determined on the number of animals in brackets. (i–k) Effects of pH 6.0 PBS, APETx2, capsazepine, and A‐317491 (i), or EAP, contralateral EAP, sham EAP, and moxibustion (j), or contralateral EAP, and EAP at a non‐acupoint (k) determined in pH 6.0 PBS and expressed as a percentage of the normal PBS (pH 7.4; 100%) effect at 0 min. As controls, the effects of pharmacological antagonists and acupuncture‐family treatments were also measured, when applied together with normal PBS (pH 7.4) (i,j). Mean ± SEM of the indicated number of experiments. APET, APETx2; CAPSAZ, capsazepine; A31, A‐317491; EAP, electro‐acupuncture; SHAM, sham EAP; MOXI, moxibustion; contEAP, contralateral EAP; nonEAP, EAP applied to a non‐acupoint. * P < .05, significantly different from the mean PWL measured at 0 min after PBS (pH 7.4) injection. § P < .05, significantly different from the effect of pH 6.0 PBS injection; Kruskal–Wallis one‐way ANOVA on ranks (H = 50,872, i; H = 45,893, j; H = 29,398, k) followed by Dunn's test
