Figure 5.
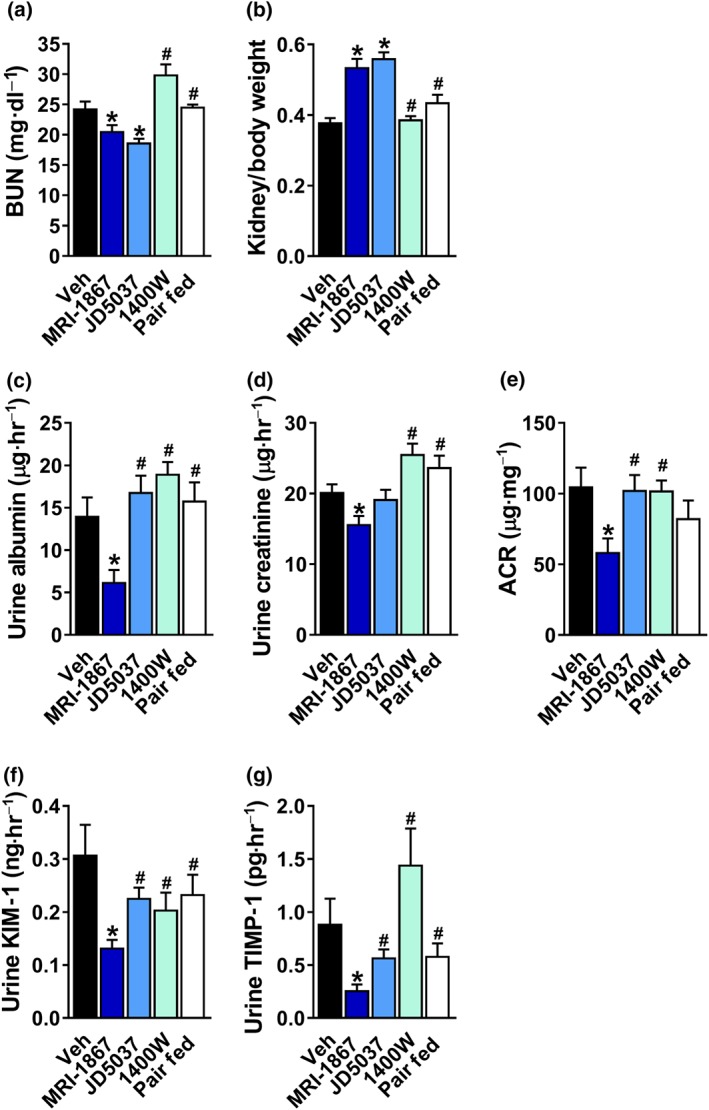
A greater efficacy of MRI‐1867 in restoring kidney function in diet‐induced obese mice in comparison with peripheral CB1 receptor blockade, inducible NOS inhibition, or pair feeding. MRI‐1867 or JD5037 treatment reduced (a) BUN levels and (b) the kidney‐to‐body weight ratio. Only MRI‐1867 was effective in reducing urinary (c) albumin, (d) creatinine, and (e) the albumin‐to‐creatinine (ACR) ratio, as well as the urinary secretion levels of (f) kidney injury marker 1 (KIM‐1) and (g) tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 (TIMP‐1). Data represent the mean ± SEM from 7 to 14 mice per group. * P < .05, significantly different from diet‐induced obese animals treated with Veh; # P < .05, significantly different from diet‐induced obese mice treated with MRI‐1867; one‐way ANOVA, followed by a Bonferroni post hoc test
