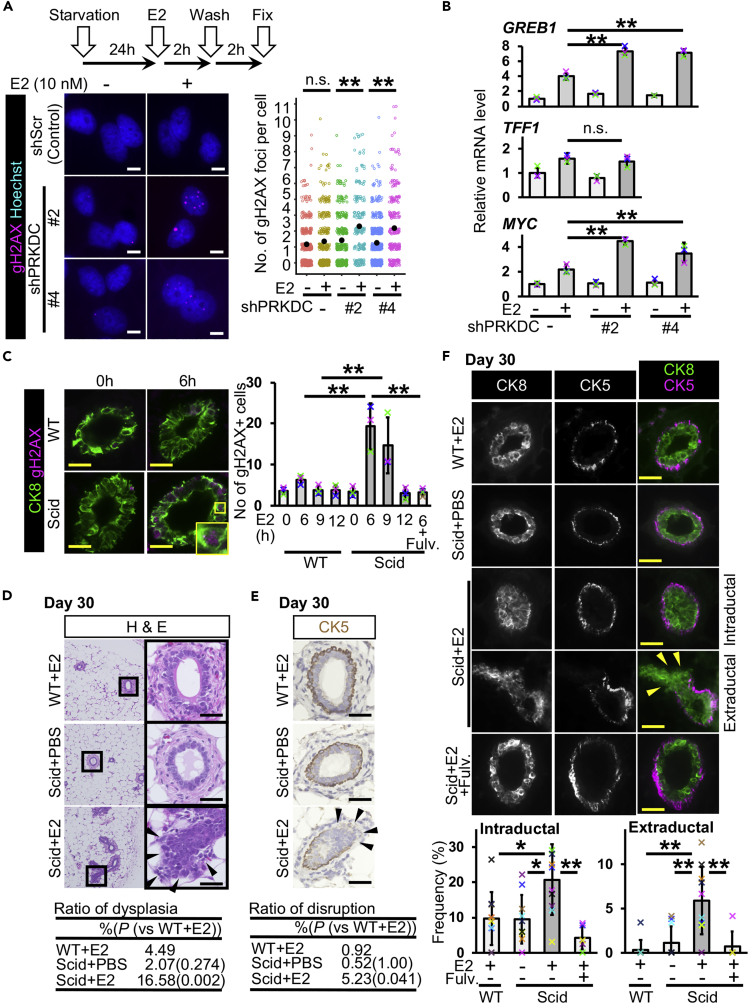
Figure 1.
Estrogen Administration Induces Mammary Ductal Dysplasia in scid Mice
(A) DNA double-strand breaks were detected in MCF-7 cells. PRKDC was knocked down. Gamma-H2AX was immunostained. Numbers of gH2AX foci per cell were graphed (jitter plot). Black dots indicate mean values. Data were obtained from 2 or 3 independent experiments (total 200–520 cells in each group, U Mann-Whitney test).
(B) Messenger RNA levels of GREB1, TFF1, and MYC were quantified (n = 3 experiments, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's test). Cells were treated with or without E2 for 6 h.
(C) Gamma-H2AX-positive mammary epithelial cells were detected and quantified at 6, 9, and 12 h after E2 administration (n = 3 mice in wild-type [WT] + E2 0 h, 6 h, 9 h, 12 h and scid + E2 0 h, 6 h, 9 h, 12 h; n = 4 mice in scid + E2 + fulvestrant 6 h, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's test).
(D) Typical images of H&E staining are shown. Daily injection of E2 was performed for 30 days. The table shows ratios of dysplasia (n = 6 mice [one image from each mouse, total six images], WT + E2 4.49%, scid + PBS 2.07% [p = 0.274, versus WT + E2], and scid + E2 16.58% [p = 0.002, versus WT + E2], U Mann-Whitney test).
(E) Typical immunostaining images of CK5 are shown. The table shows ratios of disruption (n = 6 mice [one image from each mouse, total six images], WT + E2 0.92%, scid + PBS 0.52% [p = 1.00, versus WT + E2], and scid + E2 5.23% [p = 0.041, versus WT + E2], U Mann-Whitney test).
(F) Fluorescent images of CK8 and CK5 staining are shown. Mammary ducts with intraductal and extraductal expansion were quantified (n = 10 mice in WT + E2, scid + PBS and scid + E2 groups, n = 6 mice in scid + E2+Fulv. group, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's test and U Mann-Whitney test). Fulv., fulvestrant. Scale bars, 10 μm in (A) and 30 μm in (C–F). n.s., not significant, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. Error bars represent standard deviation. Arrowheads indicate mammary epithelial cells in extraductal region (D–F). In the graphs, crosses with different colors indicated the values of different samples (B) and animals (C and F).