Figure 4.
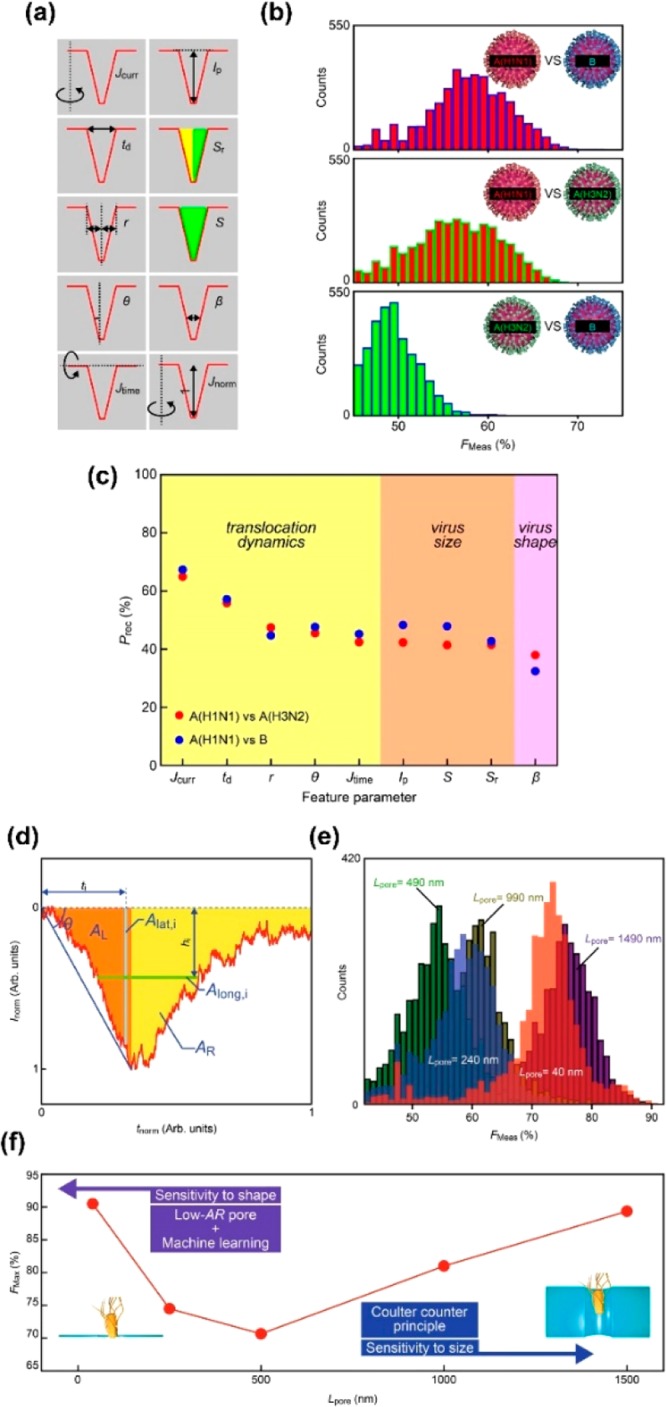
Combination of nanopore method and machine learning. (a)–(c) Identification of influenza virus. Reproduced with permission from ref (14). Copyright 2018 Springer Nature. (a) Definition of feature values used. (b) Identification accuracy for influenza A, influenza B, and influenza A subtype. The accuracy is represented by the F-measure. (c) Correlation between feature and recall. The feature indicating the flow dynamics of the virus gives high identification accuracy. (d)–(f) Discrimination between E. coli and Bacillus subtilis. Reproduced with permission from ref (16). Copyright 2017 Springer Nature. (d) Definition of feature used. (e) Dependence of nanopore thickness on identification accuracy. The identification accuracy is represented by the F-measure. (f) Nanopore thickness dependence of maximum discrimination accuracy.
