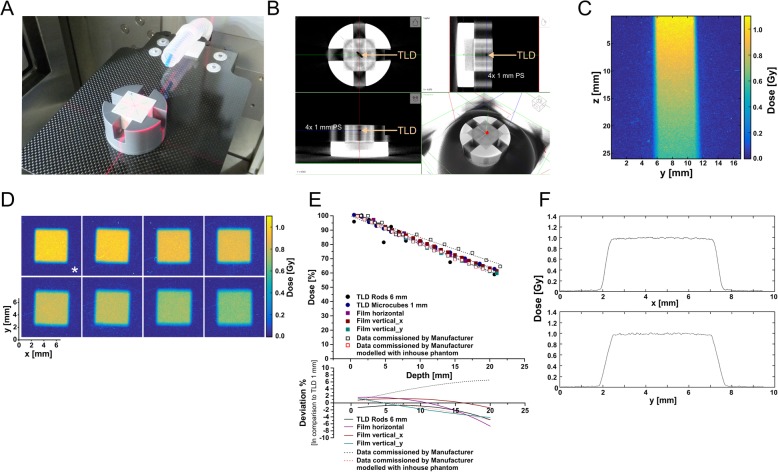
Fig. 1.
Depth dose measurements on the small animal radiotherapy platform. a The used mouse surrogate phantom consisting of a series of 1 mm polystyrene (PS) slices with fitted cavities to carry either rod-like or microcube-type thermoluminescence dosimeters (TLDs), or GAFchromic EBT3 dosimetry films, respectively. b A conebeam CT (CBCT) scan of the phantom shown in (a). c Acquisition of depth dose data in the continuous, vertical film positioning mode. d Acquisition of depth dose data in the horizontal film positioning mode. The asterisk indicates the film from which the penumbra data in (f) were extracted. e Depth dose curves obtained with the phantom shown in (a, b), for 5× 5 mm2 beam collimation, and the indicated dosimetric devices in comparison to commissioning data provided by the manufacturer (as measured by the manufacturer and calculated with the point dose calculator tool PDC 1.2 (X-Strahl) modelling the inhouse phantom used). The lower graph depicts the deviation in dose [%] as determined by the different detection methods in comparison to 1 mm3 microcube TLDs. f The lateral penumbra of the irradiation beam with 5× 5 mm2 collimation in x- and y-direction as extracted from the film marked with an asterisk in (d)