Figure 3.
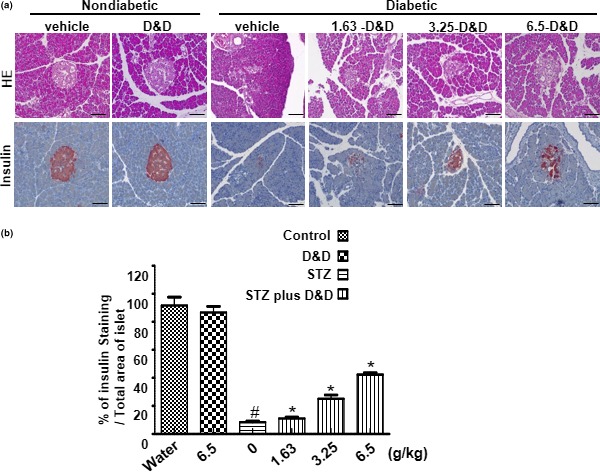
Effects of Gryllus bimaculatus powder on pancreatic function and morphology. Eight‐week‐old rats were injected intraperitoneally with a single dose of freshly prepared STZ (65 mg/kg). The control group was injected with an equal volume of citrate buffer only. After confirming the diabetic condition, the control group was fed a high dose of the Gryllus bimaculatus powder (6.5 g/kg), whereas the diabetic group was fed varying doses of the powder (1.63, 3.25, and 6.5 g/kg) twice daily. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) immunohistochemistry (top; ×200 magnification) and immunohistochemical staining with an anti‐insulin antibody (bottom; ×200 magnification) of isolated pancreases from the vehicle and Gryllus bimaculatus powder‐administered nondiabetic rats and from the vehicle and Gryllus bimaculatus powder‐administered diabetic rats (a). Quantification analysis of the positive insulin staining pancreatic islets (b). Values are means ± SEM. n = 3; # p < .05 versus control groups; *p < .05 versus STZ groups
