Figure 2.
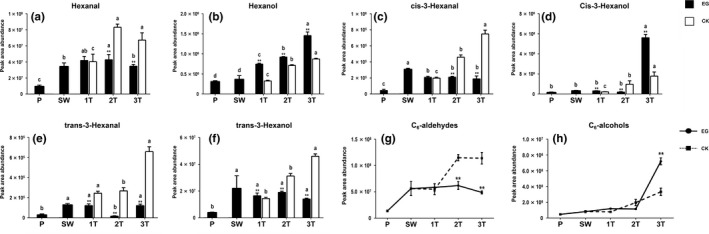
Changes in C6‐aldehyde and C6‐alcohol levels during postharvest process of oolong tea. Samples were obtained at each stage of the manufacturing process (P, fresh leaves; SW, solar withering; 1T, the first turnover (and control); 2T, the second turnover (and control); 3T, the third turnover (and control)). The relative amounts of six kinds of C6‐compounds, hexenal (a), hexanol (b), cis‐3‐hexenal (c), cis‐3‐ hexenol (d), cis‐3‐hexenal (e), and trans‐2‐hexenol (f), were detected. The total amounts of C6‐aldehydes (g) and C6‐alcohols (h) were detected. Note: One or two asterisks denote a statistically significant difference (*p < .05; **p < .01) in relative amount between the EG group and the CK group at the same sample time. Values within the same stage followed by the same letter do not differ significantly (p > .05). Error bars indicate the standard error (SE) of the mean
