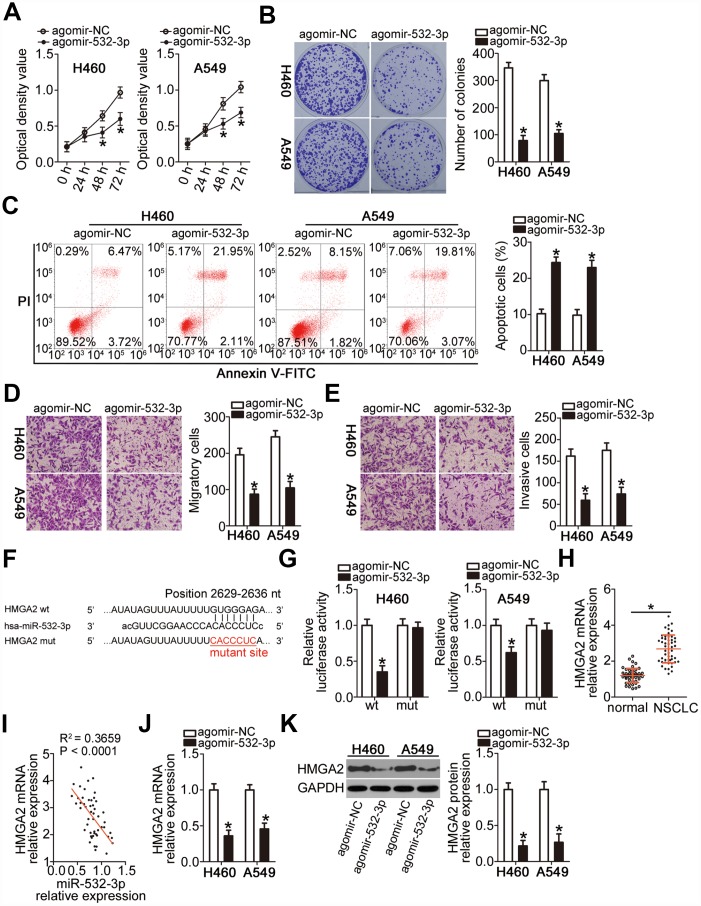
Figure 4.
miR-532-3p directly targets HMGA2 mRNA to inhibit the malignant phenotype of NSCLC cells. (A–C) Cell proliferation, colony formation, and apoptosis parameters determined by the CCK-8 assay, the colony formation assay, and flow cytometry in H460 and A549 cells transfected with agomir-532-3p or agomir-NC. *P < 0.05 vs. the agomir-NC group. (D, E) Migratory and invasive capabilities of H460 and A549 cells after transfection with agomir-532-3p or agomir-NC analyzed by the Transwell migration and invasiveness assays. *P < 0.05 vs. the agomir-NC group. (F) Wild-type and mutant miR-532-3p-binding site in the 3′-UTR of HMGA2 mRNA. (G) Relative firefly luciferase activity determined in H460 and A549 cells at 48 h after co-transfection with agomir-532-3p or agomir-NC and HMGA2-wt or HMGA2-mut. *P < 0.05 vs. the agomir-NC group. (H) RT-qPCR analysis of HMGA2 mRNA expression level in 51 pairs of NSCLC samples and corresponding normal lung tissues. *P < 0.05 vs. normal lung tissue. (I) Negative correlation between HMGA2 mRNA and miR-532-3p levels in NSCLC tissue samples revealed by the Spearman’s correlation analysis (R2 = 0.3659, P < 0.0001). (J, K) HMGA2 gene and protein expression levels in H460 and A549 cells determined by RT-qPCR and western blot, respectively, following transfection with agomir-532-3p or agomir-NC. *P < 0.05 vs. the agomir-NC group.