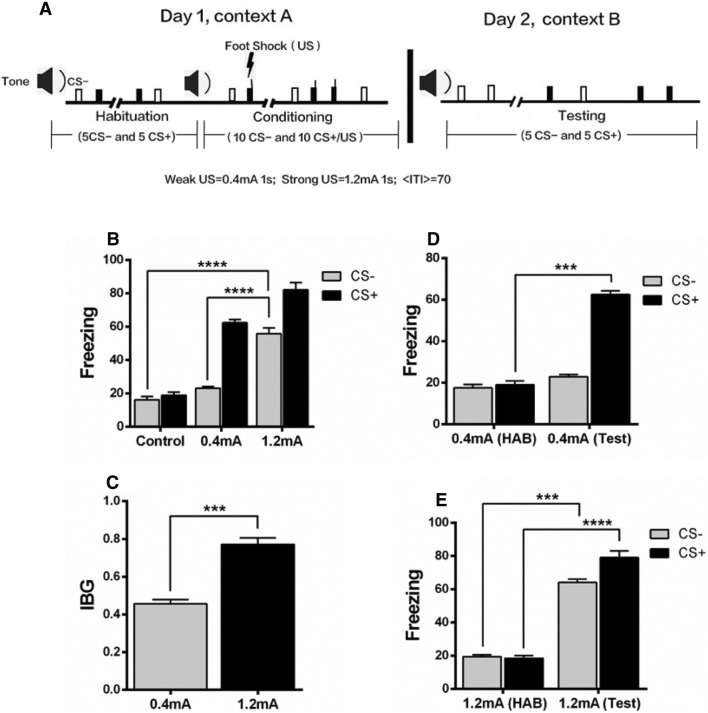
Fig. 1.
A strong shock causes fear generalization. A Schematic of the behavioral protocol. B Mice with the strong shock (1.2 mA) showed a greater freezing level to the CS– (Clicks tone, which was not paired with shock during training) tone than those with the weak shock (0.4 mA) and controls (0 mA). C The index of behavioral generalization (IBG) was higher in the strong shock group than in the weak shock group. D In the weak shock group, the fear response to a CS+ (Continous tone, which was paired with shock during training, but not paired with shock during behavioral testing) tone during the behavioral test (Test) was significantly higher than that of the habituation session (HAB); while there was no significant difference in the fear response to the CS– tone between HAB and Test. E The strong shock group showed an increased freezing level in response to both the CS– and CS+ tones, indicating fear generalization. n = 8–10 mice/group; mean ± SEM; ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.