Fig. 2.
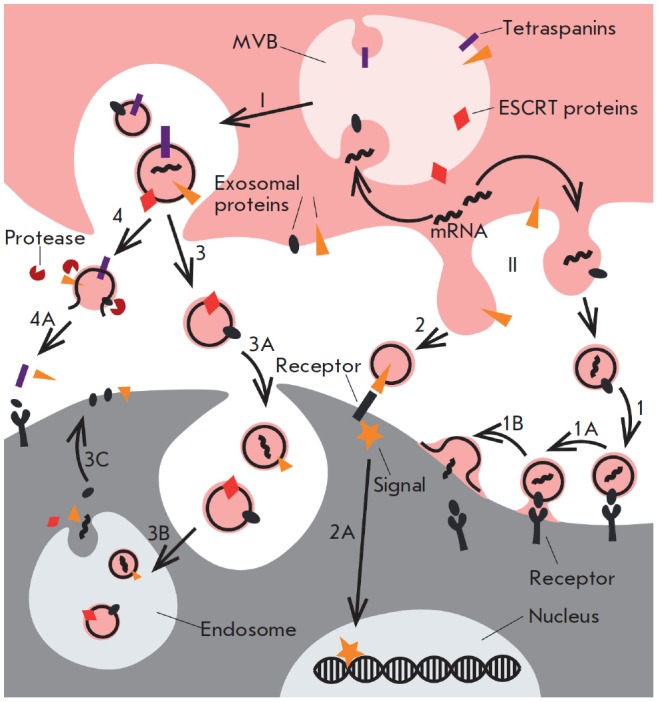
Biogenesis of EVs and their uptake by the target cells. The EV biogenesis pathways (I, II). I – EV biogenesis in MVBs via the ESCRT-dependent/ESCRT-independent pathways: fusion of MVBs with the plasma membrane; II – EV formation by direct budding from the plasma membrane into the extracellular space. The interaction between the secreted membrane vesicles and recipient cells (1, 2, 3, 4). 1, 2 – Binding of secreted vesicles to the surface of a recipient cell involves interactions between exosomal ligands and cellular receptors, fusion with the plasma membrane (1A) and release of vesicle components into the cytoplasm (1B); 2A – activation of signal pathways; 3A – vesicle endocytosis; 3B – fusion of the endocytosed exosomes with the limiting membrane of the endosome; 3C – incorporation of exosome membrane proteins into the endosome membrane, which could then be recycled to the cell surface; 4 – exosome degradation by extracellular proteases; 4A – interactions between exosomal ligands and cellular receptors
