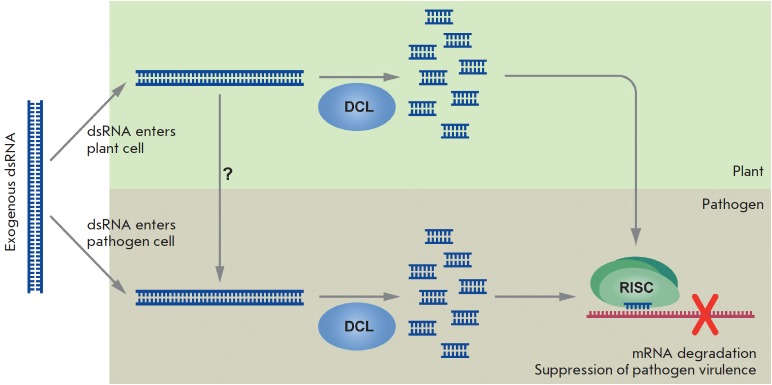
Fig. 2.
Schematic representation of the use of exogenous dsRNA for RNA interference induction and degradation of target plant pathogen mRNAs. Exogenous artificial dsRNA is dissolved and applied to plant leaves, flower buds, roots, or seeds. Uptake and transport of exogenous dsRNAs occur through an undefined mechanism. dsRNA or hpRNA molecules are recognized by DICER-like (DCL) ribonuclease that cleaves long dsRNAs into siRNAs. siRNAs are then incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) that guides sequence-specific degradation or translational repression of homologous pathogen mRNAs. Arrows depict different steps of the RNAi induction process and dsRNA/ siRNA movement between plant cells and plant pathogens