Figure 3.
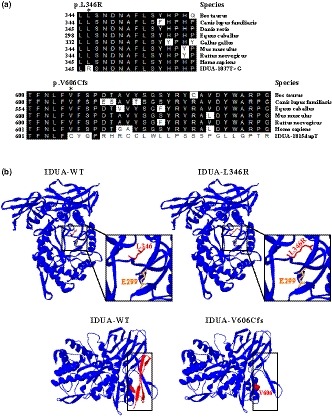
Analysis of IDUA mutation. (a) Evolutionary conservation of amino acid residues altered by c.T1037G (p.L346R) and c.1815dupT (p.V606Cfs51*) across different species. NCBI accession numbers are as follows: Bos Taurus (NP_001179665); Canis lupus familiaris (XP_538109); Danio rerio (XP_001923689); Equus caballus (XP_001492699); Gallus gallus (XP_420183); Mus musculus (NP_038491); Rattus norvegicus (NP_001102290); Homo sapiens (NP_000160). (b) The mutant proteins were structured by Swiss‐Model online software compared to the wild‐type. Ribbon representation of the human IDUA and map of the studied variant localization obtained by homology modeling analysis. The wild‐type and mutant monomers are shown in blue. Amino acid L346 and enzyme activity site E299 are shown as red and yellow stick, respectively. And, amino acid V606 is shown as red ball. The lost Ig‐like domain resulted from the frameshift mutation (c.1815dupT, p.V606Cfs51*) is shown by red ribbon in wild‐type
