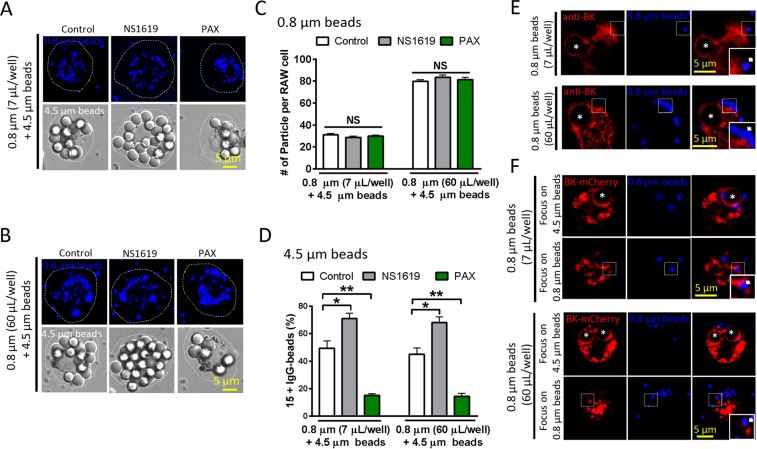
Figure 3.
BK channels regulating large particle uptake is not due to particle loading volume. (A) Representative images of RAW264.7 cells co-loaded with 4.5 μm beads and moderate dose (7 μL/well) of 0.8 μm beads. (B) Representative images of RAW264.7 cells co-loaded with 4.5 μm beads and saturate dose (60 μL/well) of 0.8 μm beads. (C) Neither NS1619 nor PAX had effect on the uptake of 0.8 μm beads when RAW264.7 cells were co-loaded with 4.5 μm beads and moderate dose of 0.8 μm beads or saturate dose of 0.8 μm beads. (D) Both NS1619 and PAX had effect on 4.5 μm bead ingestion when RAW264.7 cells were co-loaded with moderate dose of 4.5 μm beads and moderate or saturate dose of 0.8 μm beads. Cells were pre-treated with NS1619 (20 μM) or PAX (1 μM) for 30 min. (E) Endogenous BK was only recruited to the surface of 4.5 μm beads (asterisks) but not 0.8 μm beads (arrows, at both moderate and saturate doses) after co-loading for 5 min in RAW264.7 cells. (F) Exogenous BK was recruited to the surface of large (4.5 μm) beads but not small (0.8 μm, at both moderate and saturate doses) beads. Asterisks indicate the center of the 4.5 μm beads, and arrows indicate the location of 0.8 μm beads. For particle ingestion, experiments were repeated three times with triplicated samples each time for all conditions. Totally, 150–200 cells were counted for each condition.