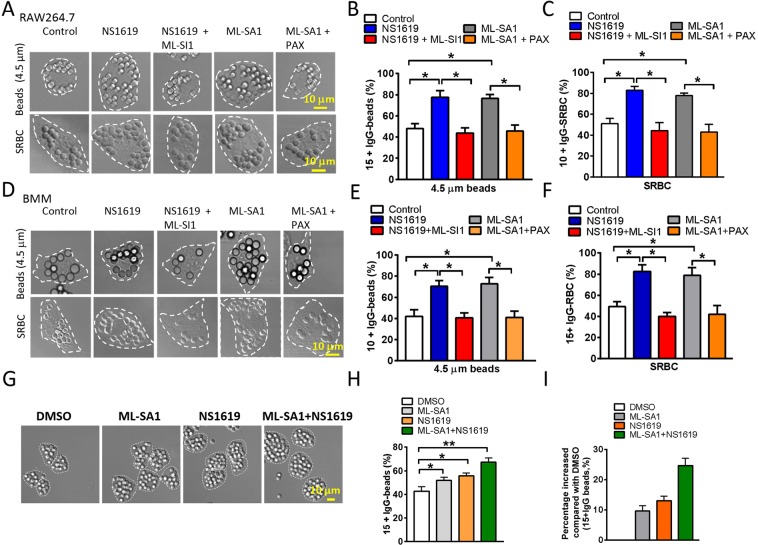
Figure 4.
Enhanced phagocytosis by BK activation requires TRPML1 function. NS1619 (20 μM) and ML-SA1 (10 μM) treatment increased large particle ingestion in RAW264.7 cells (A–C) and BMMs (D–F). Co-applying TRPML1 inhibitor ML-SI1 (10 μM) abolished the effect of NS1619. Blocking BK by Paxiline (3 μM) treatment also inhibited ML-SA1’s effect. These data suggest that BK and TRPML1 are strongly coupled to regulate large particle ingestion. (G–I) Additive effect of NS1619 and ML-SA1 on the uptake of 4.5 μm beads in RAW264.7 cells. RAW264.7 cells were pre-treated with 5 μM NS1619 or 3 μM ML-SA1 or both for 30 min, and then incubated with opsonized 4.5 μm polystyrene beads at 37 °C for 60 min. Note that, after removing the DMSO background, the combination of ML-SA1 and NS1619 produced an effect similar to the sum of their individual effects (9.667 ± 1.667 for ML-SA1, 13 ± 1.528 for NS1619, and 24.67 ± 2.333 for ML-SA1 and NS1619 combined). For particle ingestion, experiments were repeated three times with triplicated samples each time for all conditions. Totally, 150–200 cells were counted for each condition.