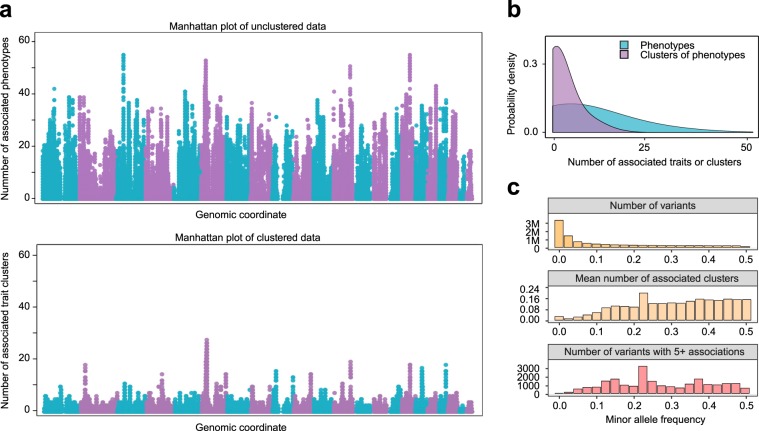
Figure 2.
Clustering of similar traits significantly reduces the number of multiple associations. (a) Manhattan plot of the number of associations per SNP in the unclustered (top) and clustered (bottom) data. (b) Comparison of the numbers of associations per SNP before and after clustering of phenotypes by phenotypic correlation. (c) Summary statistics of associations for variants with different minor allele frequency. Values are aggregated over bins of size 0.025.