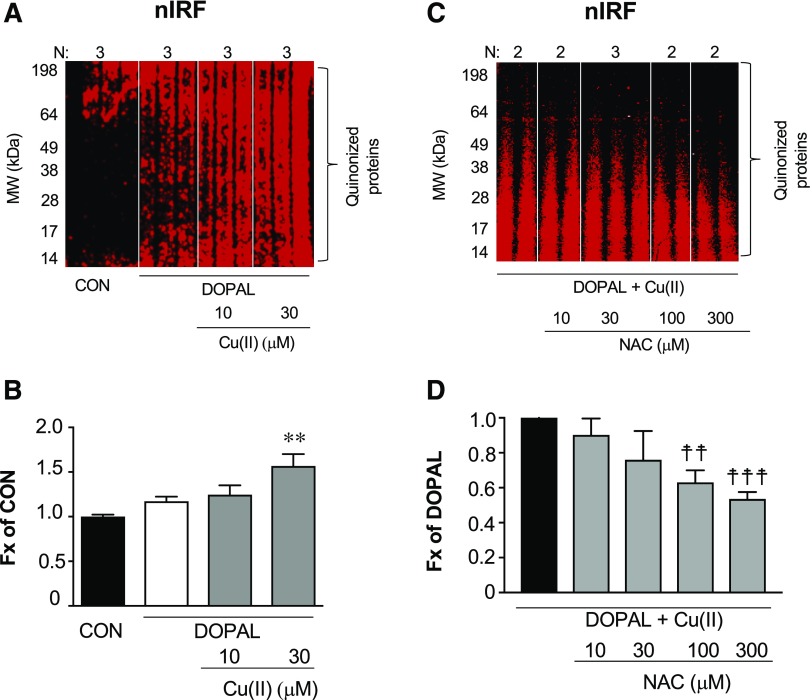
Fig. 6.
DOPAL-induced quinonization of intracellular proteins in MO3.13 cells and NAC effect. (A and B) MO3.13 cells (1.5 × 105 cells/well) were exposed to DOPAL (100 μM) or DOPAL + Cu(II) (10 and 30 μM) for 24 hours and then lysed in radioimmunoprecipitation assay buffer with protease inhibitors. (C and D) MO3.13 cells were exposed to DOPAL and 30 µM Cu(II), with NAC (0–300 μM) added at the start of incubation. DOPAL-quinonized proteins were detected and quantified by nIRF spectroscopy (red). Fx, fractions of integrated intensities of each column compared with CON (B) or DOPAL alone (D) groups normalized to the protein of each lanes. N, number of replicates. Statistical analyses were done by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-hoc test. Mean values are expressed as ± S.E.M. **P < 0.001 compared with DOPAL alone; ☨☨☨P < 0.001; ☨☨P < 0.01 compared with no NAC. Cu(II) augmented DOPAL-induced quinonization of intracellular proteins and NAC attenuated these effects.