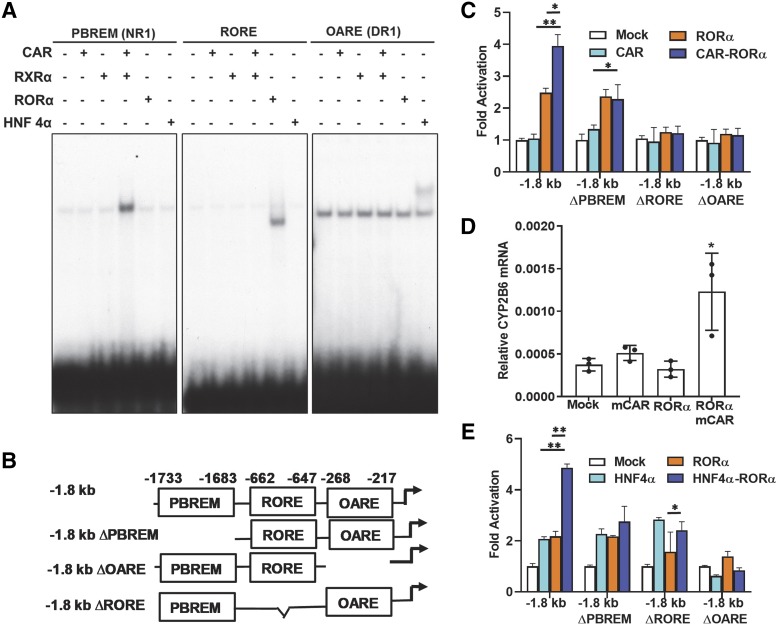
Fig. 2.
RORα coactivated CYP2B6 promoter with CAR or HNF4α. (A) RORα binding DNA element in CYP2B6 promoter was identified by gel shift analyses. Gel shift assay was performed as in Materials and Methods using 32P labeled DNA probes shown in Table 1. The assay revealed RORα bound to its putative RORE in CYP2B6 promoter. CAR and HNF4α bound NR1 and DR1, respectively, as previously reported (Sueyoshi et al., 1999; Inoue and Negishi, 2008). (B) Luciferase reporter constructs used in this study. Three elements (PBREM, 2B6-RORE, and OARE) in CYP2B6 gene promoter and their locations relative to transcriptional start site are shown. (C) RORα and CAR coactivated CYP2B6 reporter genes in COS-1 cells. RORα and CAR coactivation was observed only with the intact −1.8 kb CYP2B6 promoter. Statistical analysis was performed with values between single-factor and two-factor cotransfection. (D) RORα and CAR synergistic activation of CYP2B6 gene. CAR, RORα, or both were transfected into Huh7 cells, and CYP2B6 mRNA expression was measured from total RNAs. (E) RORα and HNF4α coactivated CYP2B6 reporter genes in COS-1 cells. HNF4α and CAR coactivation was observed only with the intact −1.8 kb CYP2B6 promoter. (C and E) Statistical analysis results were shown between single-factor and two-factor cotransfection. (C–E) The asterisk (*) between the groups represents statistically significant difference (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01). Mean and S.D. are shown for each transfected group (n = 3).