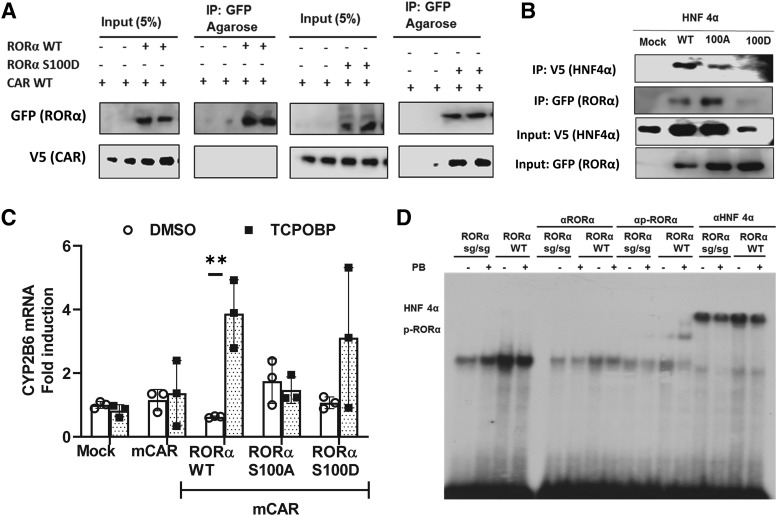
Fig. 4.
p-Ser100 RORα functional interaction with CAR and HNF4α. (A) RORα S100D mutant interacted with CAR. Coimmunoprecipitation assay was performed in Huh7 cells transiently expressing RORα WT or its phosphomimetic mutant, RORα S100D, in the presence or absence of CAR. CAR preferably interacted with RORα S100D. (B) HNF4α protein was destabilized by coexpression with RORα S100D. RORα WT, RORα S100A, or RORα S100D were cotransfected into Huh7 cells for a co-IP assay. (C) CYP2B6 gene coactivation by CAR and RORα S100D mutant. Expression plasmids of mCAR were transfected into HepG2 cells in the presence of RORα WT, RORα S100A, or RORα S100D, and CYP2B6 mRNA expression was measured. The asterisk (*) between the groups represents statistically significant difference (**P < 0.01). Mean and S.D. are shown for each group (n = 3). (D) HNF4α and p-Ser100 RORα binding to OARE. Gel shift analysis was performed as in Materials and Methods section using DR1 radioactive probe shown in Table 1 and mouse liver nuclear extracts. Stronger binding was observed with nuclear extracts from RORα WT mice liver than with RORα sg/sg, which lacks one exon in lateral organ boundaries domain of RORα gene. Though anti-RORα antibody blocked the gel shift, phospho-specific anti-Ser100 RORα antibody produced a super shift with only WT PB-treated mice liver nuclear extracts. Anti-HNF4α antibody supershifted the bands.