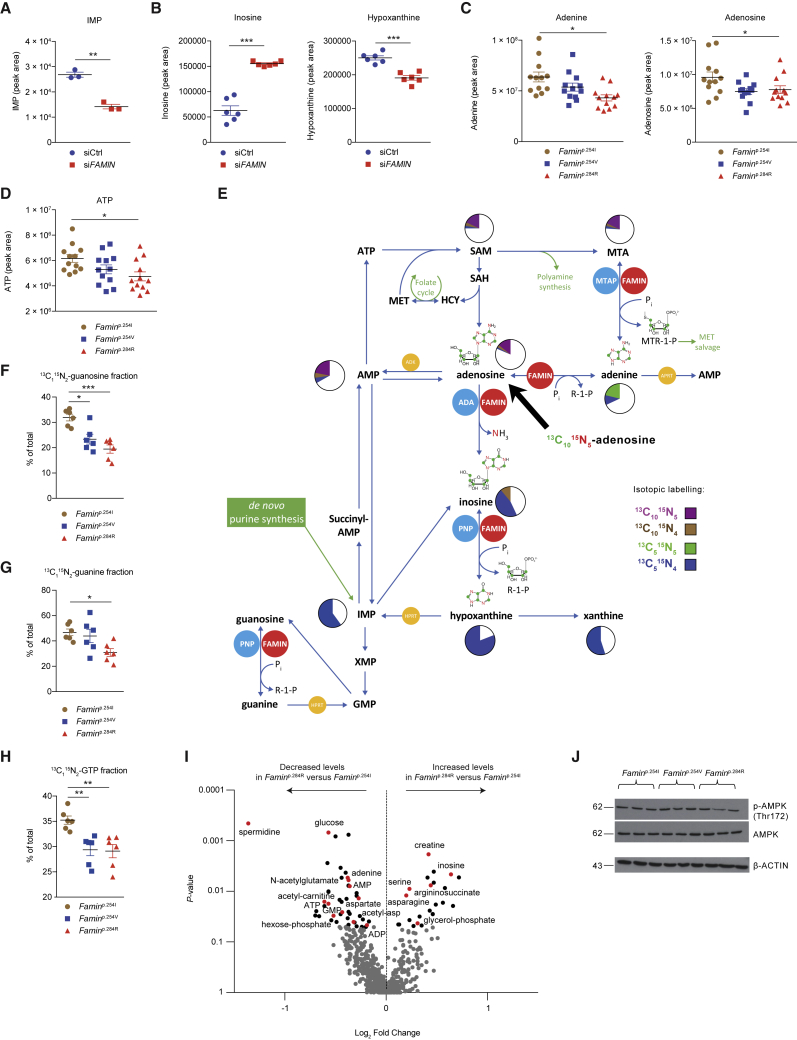
Figure 4.
FAMIN Variants Impact on Central Purine Routing
(A) IMP levels in control and FAMIN-silenced HepG2 cells 24 h after transfection (n = 3).
(B) Inosine and hypoxanthine levels in control and FAMIN-silenced HepG2 cells 48 h after transfection (n = 6).
(C and D) Adenine, adenosine, (C) and ATP levels (D) in Faminp.254I, Faminp.254V, and Faminp.284R M1 macrophages (n = 12).
(E) Metabolic fate of [13C1015N5] adenosine after a 3-h pulse of M1 macrophages (n = 6; mean). Schematic representation of central purine metabolism. Adenosine deamination into inosine releases 15N as ammonia, generating a [13C1015N4] isotopomer (brown). Phosphorolytic cleavage of inosine into hypoxanthine and [13C5] R1P, yielding the [13C515N4] isotopomer (blue). Adenosine conversion to AMP without loss of label (purple). Phosphorolytic cleavage of fully labeled MTA generates [13C515N5] adenine (green) and [13C5] 5′-methylthioribose-1-phosphate. Fractions of differently labeled states (averaged across Faminp.254I, Faminp.254V, and Faminp.284R genotypes) depicted as pie charts. ADA, adenosine deaminase; ADK, adenosine kinase; APRT, adenine phosphoribosyl transferase; HPRT, hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase; MTAP, MTA phosphorylase; PNP, purine nucleoside phosphorlyase.
(F–H) Fraction of guanosine (F), guanine (G), or GTP (H) labeled as the indicated isotopomer in M1 macrophages after a [13C115N2] guanosine pulse (n = 6).
(I) Metabolite levels (gray dots) in Faminp.254I versus Faminp.284R M1 macrophages depicted as volcano plot. False discovery rate (FDR)-controlled LC-MS features (black dots), select metabolites in red (n = 6).
(J) Immunoblots (IBs) with indicated antibodies in M1 macrophages (n = 3).
Data represented as mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001 (unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t test or one-way ANOVA).