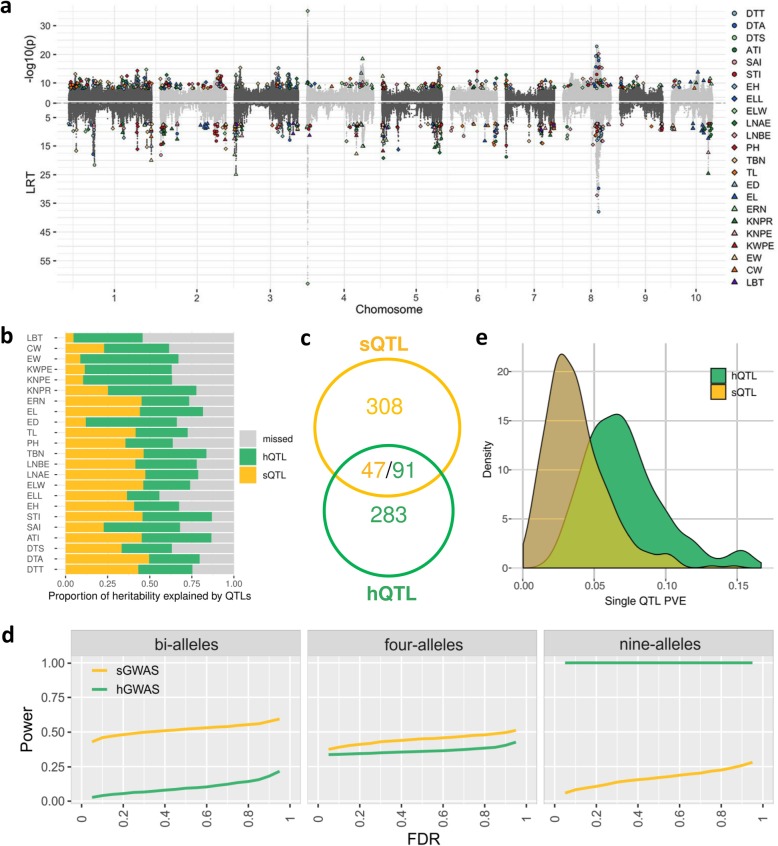
Fig. 2.
Overview of the 2 methods of GWAS analysis. a Summary porcupine plot of mapping results for 23 agronomic traits. Significant SNPs (P ≤ 1.23E−8) or bin (LRT value ≥ 7.1) at each QTL is marked by a dot, with each color corresponding to a trait. The abbreviations are defined in the “Methods” section. b The partition of heritability explained by all identified QTL. Each horizontal bar indicates heritability accounted for by sQTL (yellow), additionally by hQTL (green), and missing or unexplained (gray) relative to total heritability. c Venn diagram of co-localization between sQTL and hQTL, summed over traits. d Simulation analysis of mapping power under three QTL types. The three types of QTL were simulated to express as bi-allelic, four allelic, and nine allelic QTL, which were assumed to be produced by one, two, or 3 independent functional variants available in the local QTL region. The details of simulation analysis can be seen in the “Methods” section. e Comparison of variance explained (PVE) by single QTL identified by sGWAS vs. hGWAS