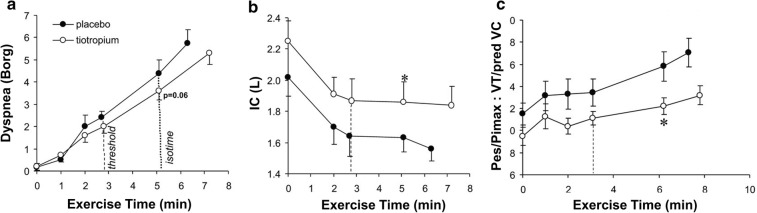
Fig. 6.
Ventilatory responses to CWR exercise between tiotropium and placebo demonstrating reduced b dynamic hyperinflation with c improved musculo-mechanical coupling and a reduced dyspnea. CWR constant work rate, IC inspiratory capacity, Pes/PImax tidal esophageal pressure relative the maximum esophageal inspiratory pressure, VT tidal volume.
Adapted from O’Donnell DE, Hamilton AL, Webb KA. Sensory-mechanical relationships during high-intensity, constant-work-rate exercise in COPD. J Appl Physiol. 2006;101(4):1025–1035