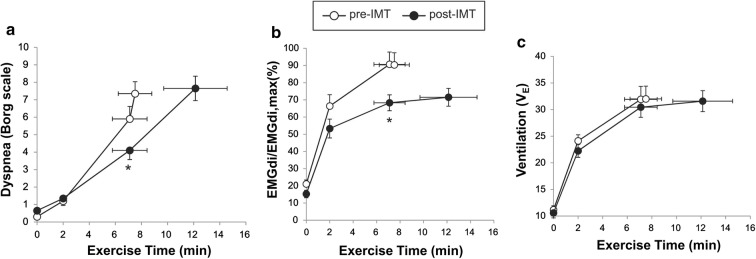
Fig. 7.
Improvement in a dyspnea, b inspiratory neural drive (EMGdi/EMGdi,max), and c ventilation following IMT in patients with COPD and evidence of inspiratory muscle weakness. COPD chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, EMGdi/EMGdi,max index of inspiratory neural drive to the crural diaphragm, IMT inspiratory muscle training, VE minute ventilation.
Adapted from Langer D, Ciavaglia C, Faisal A, Webb KA, Neder JA, Gosselink R, Dacha S, Topalovic M, Ivanova A, O’Donnell DE. Inspiratory muscle training reduces diaphragm activation and dyspnea during exercise in COPD. J Appl Physiol. 2018;125(2):381–392