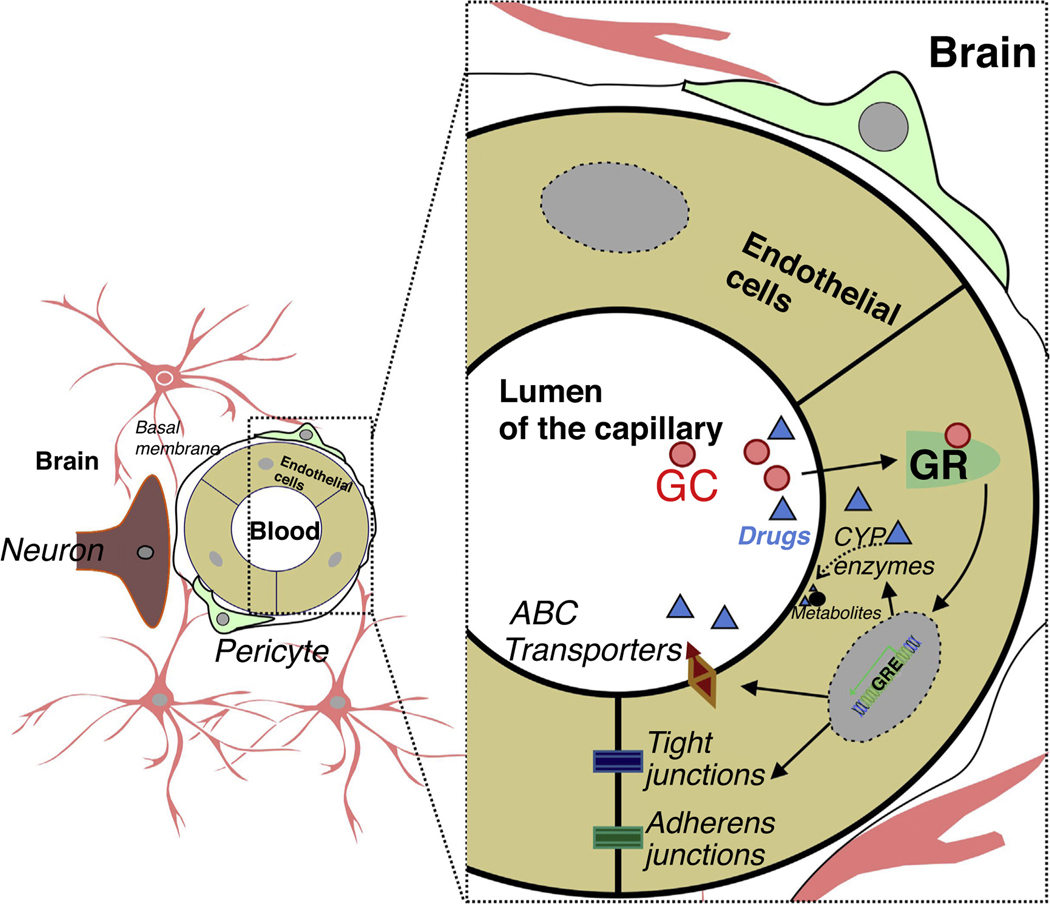
FIGURE 2.
Endothelium-specific glucocorticoid receptor (GR) function at the neurovascular unit. Glucocorticoids (GCs), or any drug as a GR ligand in circulation, diffuse across the cell membrane, bind to the GR in the cytoplasm and initiate translocation to the nucleus. Subsequent to GR modulation, the downstream events include regulation of tight-junction proteins (claudins, occluding, etc.) and adherens junction protein. Endothelial cytochrome P450 (P450 s) drug-metabolizing enzymes and ATP-binding cassette transporters/efflux drug transporters (ABC transporters), translated downstream of ligand-dependent GR activation, metabolize and/or remove xenobiotics at the blood–brain barrier, which is enhanced in pathological conditions.