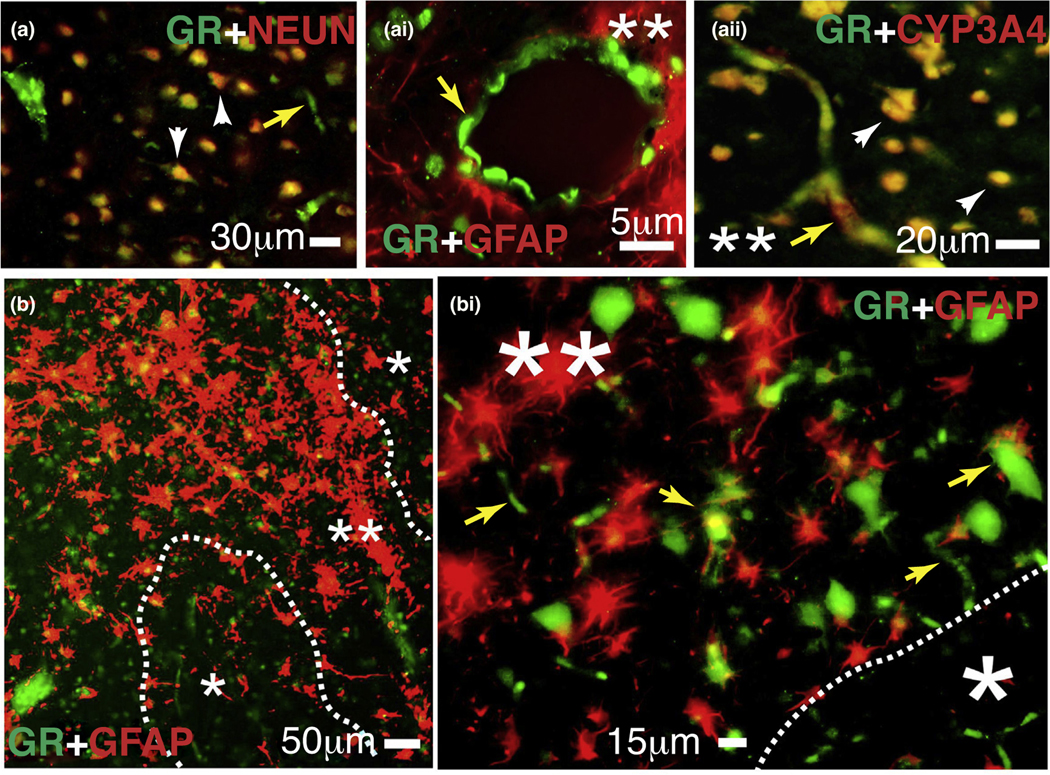
FIGURE 5.
Expression of the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) and cytochrome P450 (CYP)3A4 in human epileptic brains. (a–bi) The GR is found at the blood–brain barrier interface and in neurons in epileptic brains. Magnification of gliotic regions (**) and GFAP + staining on a resected human epileptic brain showed increased expression of GR and CYP3A4. This staining pattern was less evident in nongliotic regions (*). Note: the indicators for neurons are depicted as arrowheads and those for capillaries as yellow arrows. Colocalization was evaluated with neuronal markers (NEUN) and glial markers (GFAP). (a-ai) GR expression was observed at the vascular interface (a–ai, yellow arrows) and in neurons (a and aii). (aii) Colocalization of GR staining with CYP3A4 was found in regions with reactive gliosis (**). (b–bi) Representative images of brain samples from patients with temporal lobe epilepsy show GR staining in regions with reactive gliosis (**).