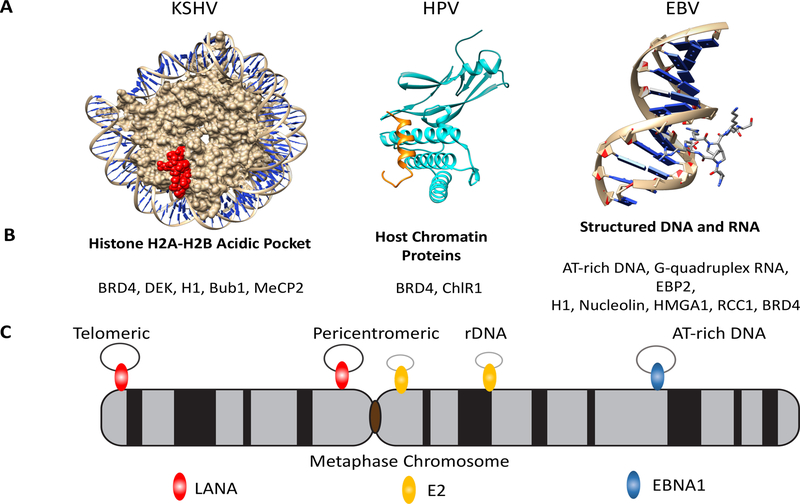
Figure 2.
Metaphase Chromosome Attachment Mechanism. (A) Crystal structures of episome maintenance protein (EMP) interactions with targets in metaphase chromosome attachments. LANA (red) N terminal peptide bound to histone H2A-H2B pocket of the nucleosome (PDB 1ZLA), HPV E2 peptide bound to BRD4 (cyan) (PDB 2NNU), and an AT-rich minor-groove binding molecule netropsin with DNA representative of the EBNA1-AT hook interactions with metaphase chromosomes (PDB 1Z8V). (B) Partial list of metaphase tethering targets for EMPs. LANA interacts with BRD4, DEK, H1, Bub1, MeCP2; E2 interacts with BRD4 and ChIR1; and EBNA1 interacts with AT-rich DNA, RNA-G quadruplex, and protein-target (EBP2, nucleolin, HMGA1, H1). (C) Depiction of the viral episome (small black rings) bound to metaphase chromosome positions by LANA (red) at peritelomeric and pericentromeric regions, E2 (yellow) bound to pericentromeric and rDNA regions, and EBNA1 (blue) bound to AT-rich DNA elements. Abbreviations: KSHV, Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus; EBV, Epstein–Barr virus; HPV, human papillomavirus.