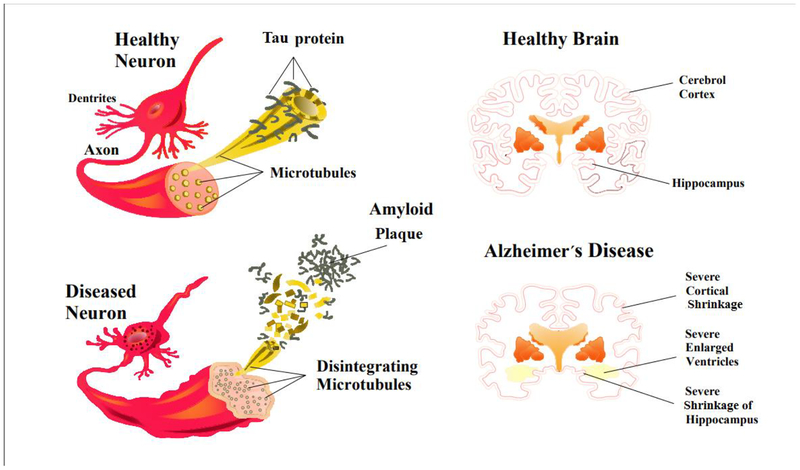
Figure 3.
A schematic showing different events in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. An alteration in tau protein leads to microtubule breakdown in brain cells. A healthy neuron and an affected neuron are shown (A, B). Tau phosphorylation contributes to the formation of neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer’s disease. In patients with Alzheimer’s disease, hyperphosphorylation of specific amino acids in the tau protein leads to the proteins dissociating from the microtubules, and forming tau tangles. At the same time extracellular amyloid plaque disturbs the transport structure and leads to starvation of neurons, and ultimately induces cell death.