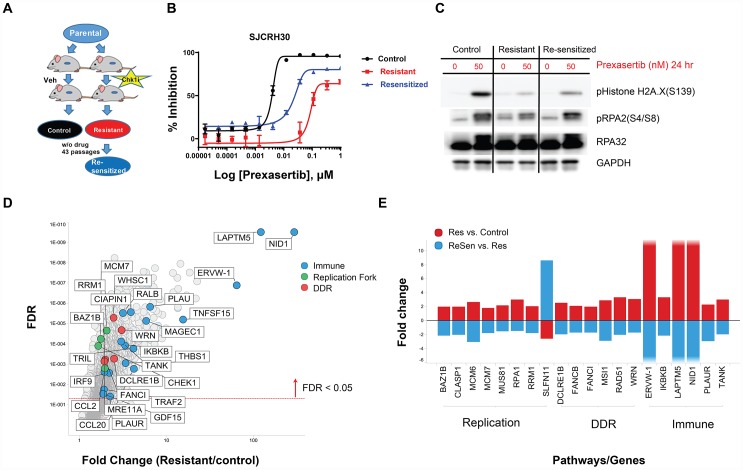
Figure 9. In vivo establishment and genomic characterization of acquired resistance to prexasertib in the aRMS SJC-Rh30 xenograft model.
(A) Schematic of the method used to generate prexasertib-sensitive and –resistant cultures from SJC-Rh30 xenografts. (B) Viability of parental SJC-Rh30, SJC-Rh30R, and SJC-Rh30reS cells assayed following prexasertib treatment and corresponding levels of markers of DNA damage (γH2AX) and replication stress (pRPA2, S4/8) following drug treatment (C). (D) Change in RNA expression levels between SJC-Rh30R and SJC-Rh30 (red) and SJC-Rh30R and SJC-Rh30reS (blue). (E) Comparison of fold change in expression values for selected DDR, immune and replication fork genes between SJC-Rh30R and SJC-Rh30reS cells.