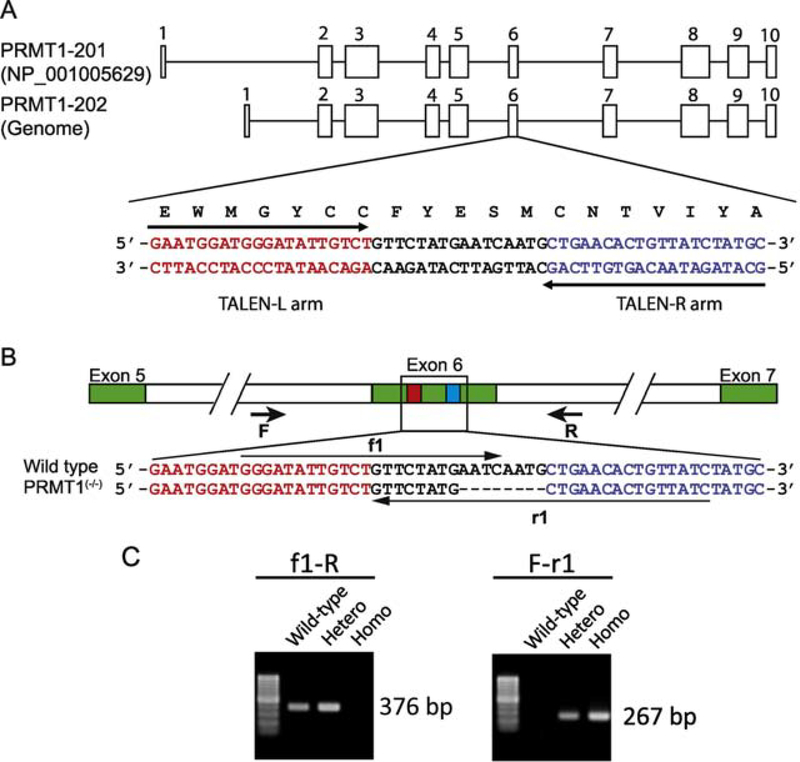
Figure 1. Generation of PRMT1 knockout Xenopus tropicalis.
(A) PRMT1 genomic structure and design of TALEN against X. tropicalis PRMT1 locus. There are two PRMT1 transcripts encoded by 10 exons each. PRMT1 specific TALEN-arms (marked with arrows) were designed to target E153 in the functional domain for di-methylation activity, in the exon 6.
(B) Schematic diagram depicting sequences of the TALEN targeted region in the wild type and a PRMT1 mutant (8 bases deletion) line. Red box and blue box in exon 6 indicate left and right TALEN arms, respectively. Arrows represent primers used for genotyping: the forward primer F and f1, and the reverse primer R and r1. Green boxes are exons.
(C) Representative examples of genotyping by PCR. Genotyping was carried out on genomic DNA by using two different primer set, primer f1 and primer R for detecting wild type allele and primer F and primer r1 for detecting the mutant allele, respectively. The presence of only wild type PCR product (376 bp) or mutant PCR product (267 bp) in the PCR reaction indicates the animals as wild type or a homozygous mutant, respectively, while the presence of both PCR products indicates a heterozygous mutant.