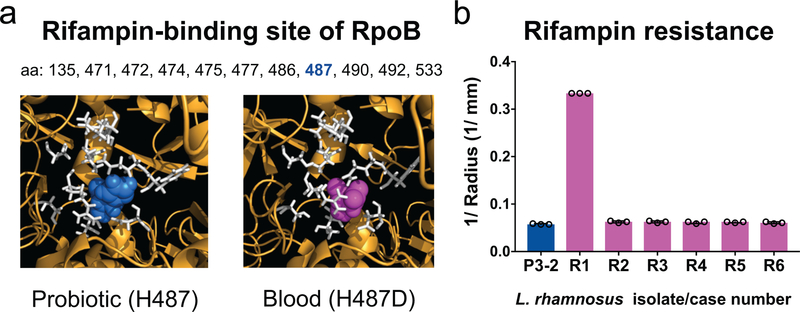
Fig 3. The Lactobacillus rhamnosus blood-isolate-specific rpoB SNP occurs at the rifampin-binding site and confers rifampin resistance.
(a) Predicted structure of L. rhamnosus GG RNA polymerase β-subunit RpoB showing the rifampin-binding site (white) with histidine 487 of the probiotic (blue, left) and aspartic acid 487 of the blood isolate from Patient R1 (magenta, right). (b) Rifampin susceptibility testing of blood isolates of each patient (R1–R6) compared to a probiotic isolate with no SNPs (P3–2). Bars depict the medians of 3 independent experiments, and error bars show the interquartile ranges. *P = 0.0021 for R1 compared to P3–2 by Kruskal- Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. The blood isolate from Patient R1 was resistant based on zone cutoffs for S. aureus (Supplementary Table 8).