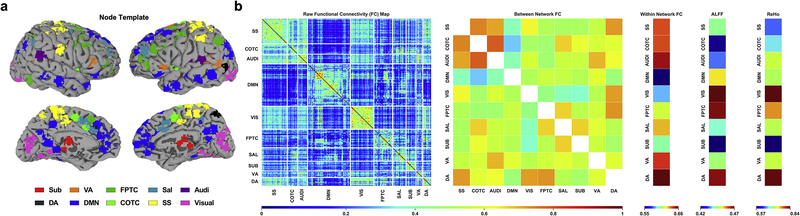
Fig 2.
Extraction of model features using fMRI-based measures of resting state activity. (a) Node template representing anatomical location of 226 seed regions of interest (ROIs) consolidated into 10 networks (Power et al., 2011): subcortical (Sub), ventral attention (VA), frontoparietal task control (FPTC), salience (Sal), auditory (Audi), dorsal attention (DA), default mode (DMN), cinguloopercular task control (COTC), sensory/somatomotor (SS), visual (Visual). (b) Raw functional connectivity map (left) generated from seed-based pairwise Pearson correlations between 226 ROIs. Activity was averaged according to network template yielding measures of between network (off-diagonal) and within network (on-diagonal) functional connectivity (middle). Two additional measures of functional segregation, the amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations (ALFF) and regional homogeneity (ReHo), were calculated independently using the network templates.