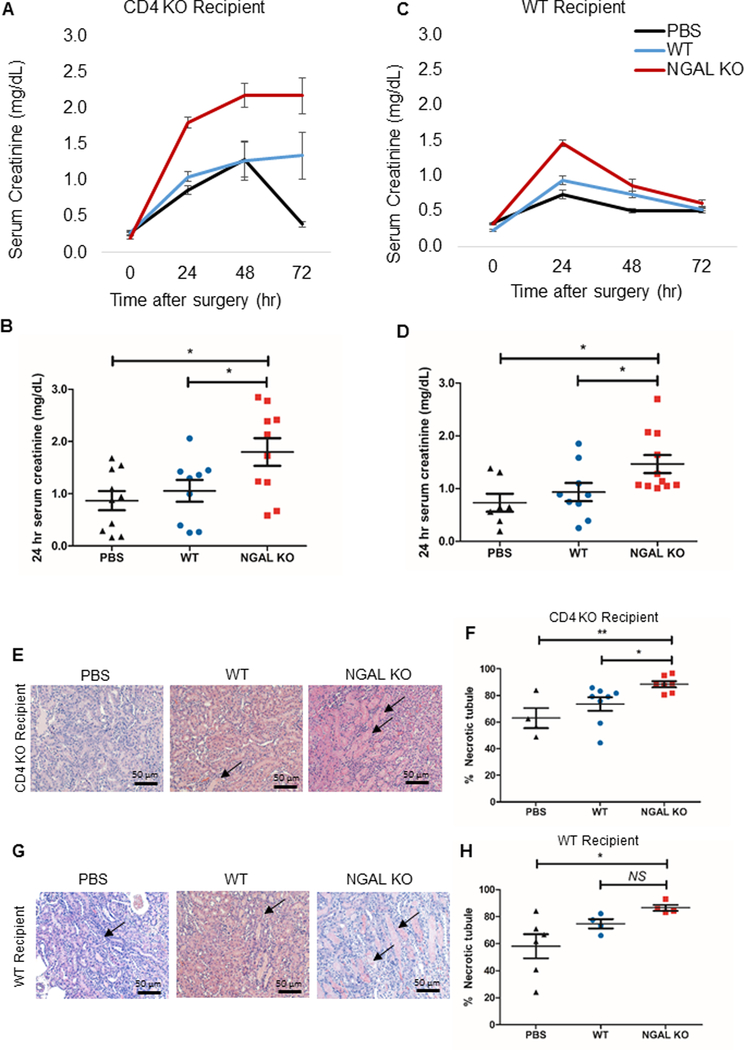
Figure 4. Adoptive transfer of Lcn2-deficient CD4+ T cells aggravates the course of AKI.
Splenic CD4+ T cells were isolated from WT or NGAL KO male mice and adoptively transferred into either CD4 KO male mice (A, B) or WT male mice (C, D) 24 hours before IRI. Adoptive transfer of splenic CD4+ T cells from NGAL KO mice led to significantly worse renal function following IRI, compared to the mice that received WT splenic CD4+ T cells or no cells (PBS) in both CD4 KO and WT recipient mice. Panel B and D show individual data points for 24 hr serum creatinine (n=7–11). (E, G) Representative images of hematoxylin and eosin-stained kidney sections of each experimental groups either in CD4 KO recipient or WT recipient (F, H) Dot plots show the percent score of necrotic tubules in outer medulla of each experimental group either in CD4 KO recipient (F) or WT recipient (H) (n=7–11). There was significantly higher necrosis in outer medullary tubules in Lcn2-deficient CD4+ T cell transferred-group compared to WT CD4+ T cell transferred-group as well as PBS control both into the CD4 KO recipient and the WT recipient, except WT recipient transferred with WT CD4+ T cell. Data presented as mean±SE. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, NS, not significant. Original magnification, x200 in E and G.