Fig. 3. Antibiotic modulation of conjugation is rare in pathogenic E. coli.
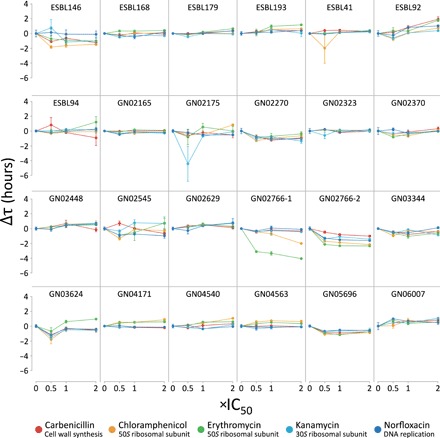
The effect of five antibiotics on conjugation in clinical E. coli pathogens was assessed via the time to threshold method. Antibiotics of differing therapeutic mechanism were dosed in three concentrations (0.5×, 1×, and 2×) based on 50% inhibitory concentrations for a MG1655 E. coli recipient standard. IC50 values for Carb, Cm, Kan, erythromycin (Ery), and Norf were as follows: 1.91, 1.92, 2.13, 20.20, and 0.05 μg/ml. Displayed Δτ are averages of triplicate measurements ±SE, and normalized by subtracting the no-antibiotic control τ. Promotion of conjugation is indicated by Δτ < 0, while Δτ > 0 indicates inhibition. Only GN02766 displayed major modulation of conjugation when exposed to Ery (all concentrations, P < 0.01, Tukey post hoc test) and Cm (2× concentration, P < 0.05). Results from two separate GN02766 experiments are shown.
