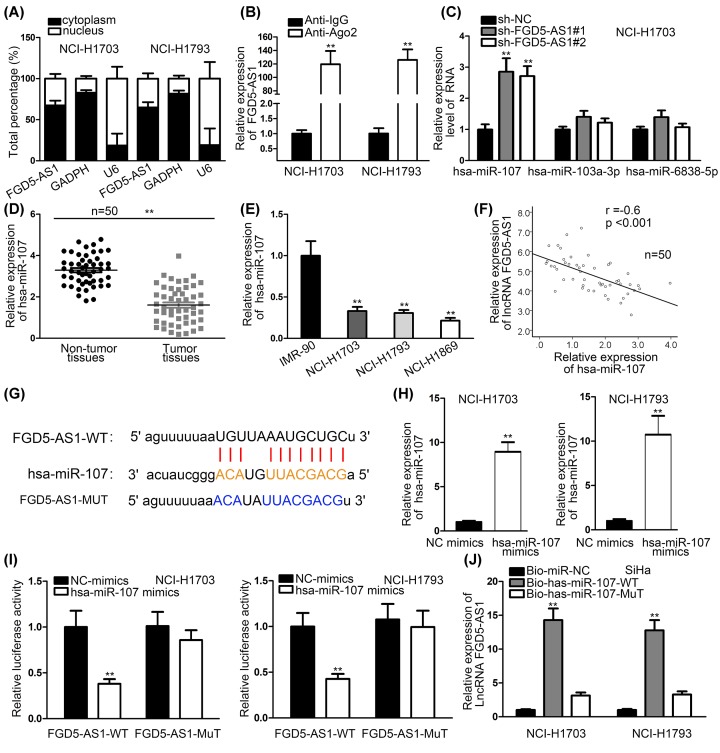
Figure 2. LncRNA FGD5-AS1 can bind to hsa-miR-107.
(A) Nuclear–cytoplasmic fractionation was implemented to prove FGD5-AS1 was in cytoplasm. (B) FGD5-AS1 enrichment in RISC was proved by RIP assay. (C) A contrast of the expression of hsa-miR-107 and other two miRNAs (hsa-miR-103a-3p and hsa-miR-6838-5p) was made by qRT-PCR analysis to find the most proper miRNA. (D) qRT-PCR analysis investigated the relative expression of hsa-miR-107 in NSCLC tissues and in normal tissues. (E) The expression of hsa-miR-107 was detected in cell lines (IMR-90, NCI-H1703, NCI-H1793 and NCI-H1869) by qRT-PCR assays. (F) The negative correlation in hsa-miR-107 and FGD5-AS1 was conducted by Kaplan–Meier method. (G) Binding sites between FGD5-AS1 and hsa-miR-107 were presented by bioinformatics. (H) qRT-PCR assays were used to detect the overexpression efficiency of hsa-miR-107 in NSCLC cell lines (NCI-H1703 and NCI-H1793). (I,J) RNA pull-down assays and luciferase reporter assays were performed to detect the binding relationship between FGD5-AS1 and hsa-miR-107 in NSCLC cell lines (NCI-H1703 and NCI-H1793). **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 indicated statistically significant differences in this figure.