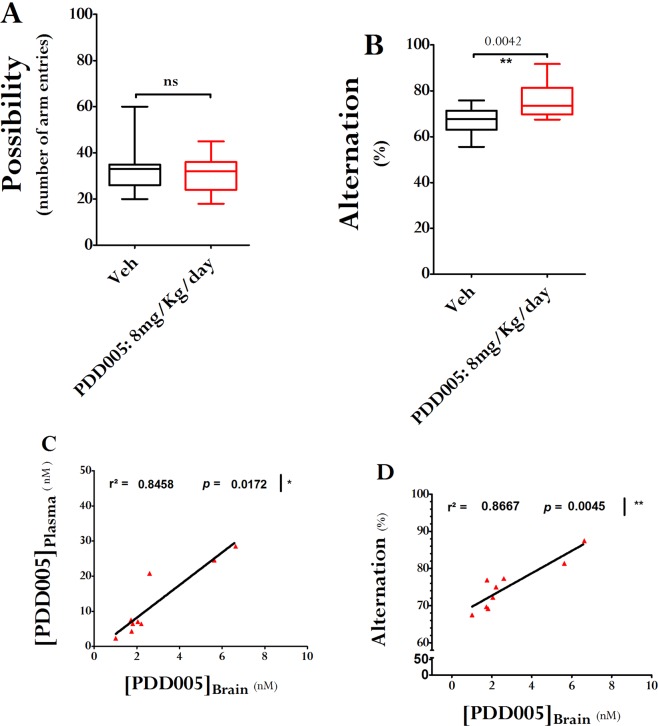
Figure 1.
PDD005 improves cognitive performance in young adult mice. Young adult WT mice were exposed by SC injection to PDD005 at 8 mg/kg/day or vehicle for 28 days. (A,B) Plots illustrating the effect of PDD005 on short-term memory (working memory) in the Y-maze 3–4 weeks after the end of treatment. (A) General activity was estimated by counting the number of arm entries. PDD005 exposition has not shown to induce hyper or hypoactivity. Cognitive abilities were assessed by the percentage of alternation (B). Mann-Whitney tests were performed and **P < 0.01 indicates significant differences between PDD005 and control conditions. Data expressed as means ± SEM with n = 15 mice/condition. (C) Linear regression analysis shows a positive correlation between brain and plasma concentration of PDD005 at 4 weeks at the end of the exposure period. (D) Linear regression analysis shows a positive correlation between brain concentration of PDD005 and short-term memory abilities at 4 weeks after the end of the treatment. Spearman tests were performed and *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.001 indicate significant correlation. Data expressed as means ± SEM with n = 9 mice/condition.