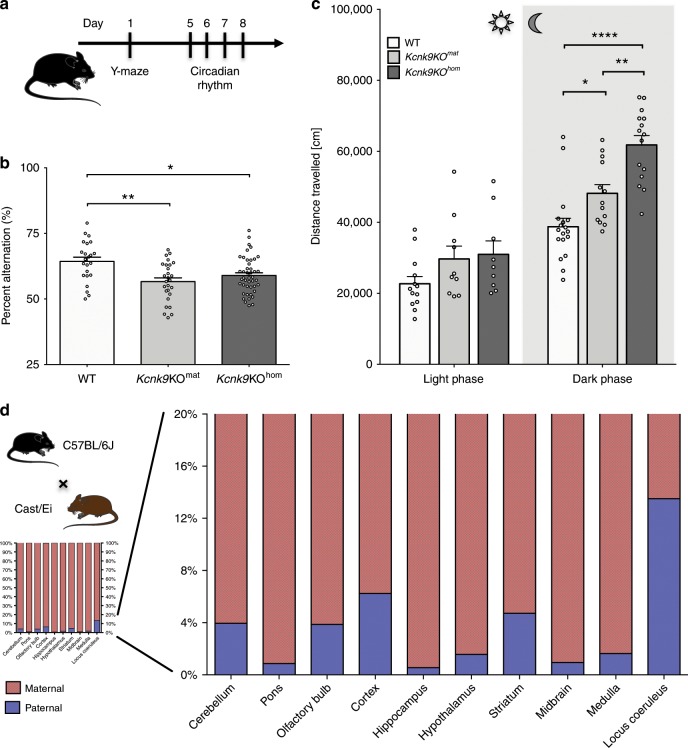
Fig. 1. Deletion of non-canonical imprinted Kcnk9 gene leads to impaired behavior of Kcnk9KO mice.
a Schematic representation of the sequence of mouse behavioral experiments. b Y-maze percentage alternation analysis of WT (n = 23), Kcnk9KOmat (n = 27), and Kcnk9KOhom (n = 44) mice. A spontaneous alternation was defined as consecutive entries into all three arms without revisiting an arm. Kcnk9KO mice display a significant decrease in percentage alteration compared with WT mice. One-way ANOVA: F(2, 91) = 7.261, P = 0.0012; followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison post hoc test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. c Total locomotor activity (distance traveled in the home cage) in light (12 h, sun symbol)/dark (12 h, moon symbol) phase. The left section shows no difference in distance traveled in the light phase of WT (n = 13), Kcnk9KOmat (n = 10) and Kcnk9KOhom (n = 9) mice. One-way ANOVA: F(2, 29) = 2.281, P = 0.1203. The right section depicts the nocturnal activity of WT (n = 18), Kcnk9KOmat (n = 13) and Kcnk9KOhom (n = 15) mice. Kcnk9KOmat and Kcnk9KOhom mice display significantly increased nocturnal hyperactivity compared with WT littermates with activity scores of Kcnk9KOmat mice intermediate between Kcnk9KOhom and WT mice. One-way ANOVA: F(2, 43) = 22.70, P < 0.0001; followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison post hoc test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001. b, c Behavioral experiments were performed in seven independent sessions. d Non-canonical Kcnk9 imprinting in (C57BL/6xCast/Ei)F1 hybrid mice. Quantification of Allele-Specific Expression by Pyrosequencing (QUASEP) of several brain regions from (C57BL/6xCast/Ei)F1 hybrid mice; maternal allele (red) and paternal allele (blue). Cerebellum n = 14, pons n = 10, olfactory bulb n = 12, cortex n = 14, hippocampus n = 14, hypothalamus n = 9, striatum n = 5, midbrain n = 5, medulla n = 5, and locus coeruleus n = 4; n = biologically independent samples. a–d Data are means ± 1 SEM (standard error of the mean). Statistical analyses and approaches are provided in Supplementary Table 1. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. The mouse images in this figure were created using Servier Medical Art templates, which are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License; https://smart.servier.com.