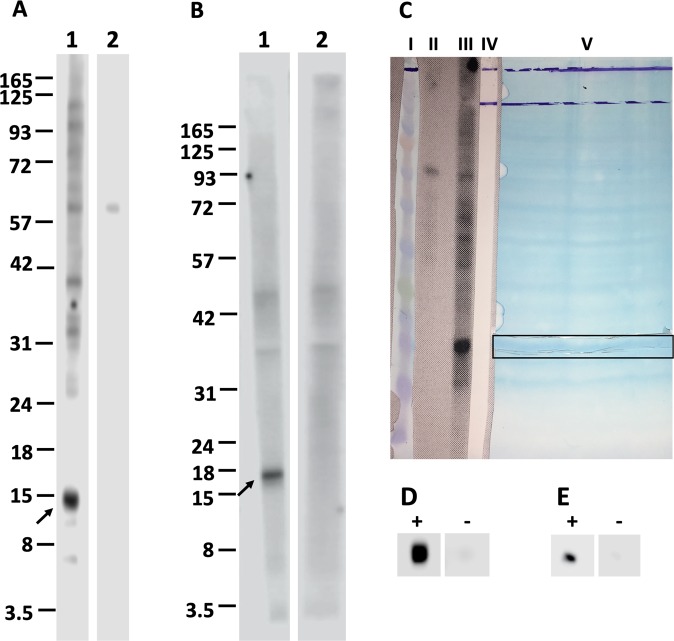
Figure 2.
Confirmation of interaction between recombinant ligands and proteins of hBMECs using Western blotting. Nitrocellulose membrane strips with transblotted proteins of hBMECs were incubated either with recombinant ligands (A1 – rDIII; B1 – rNadA) or with TBS (negative control, A2 and B2). The interaction was detected using HisProbe-HRP conjugate and visualized with chemiluminescent substrate. Arrow indicates the potential receptors of hBMECs (~15 and ~17 kDa). C shows the alignment of protein marker (lane I, BlueEye prestained protein marker, JenaBioscience), strip transblotted with hBMECs proteins incubated with TBS (lane II, negative control in Western blotting), strip transblotted with hBMECs proteins incubated with recombinant ligand in Western blotting (lane III), strip after acquisition of the chemiluminescent signals from A1 (lane IV), and the nitrocellulose membrane with transblotted proteins of hBMECs, from which 2 mm vertical strip was cut and used in the Western blotting (lane V). Horizontal strip of the nitrocellulose membrane corresponding to the potential receptors of hBMECs (~15 and ~17 kDa) was cut (outlined with horizontal frame). Small piece of horizontal strip was used to affirm the interaction with recombinant ligands. Small piece was either incubated with rDIII (D “+”) or rNadA (E “+”) or TBS (negative controls, D and E “−”) and interaction was detected using HisProbe-HRP conjugate and chemiluminescent substrate. The rest of the strip with potential was used for subsequent identification of putative receptor-binding sites on rDIII and rNadA. Original photos of the blots used to make this figure are presented in the Supplementary Figures S9, S10 and S11.