Fig. 3. H2 evolution pathways over [PtW6O24].
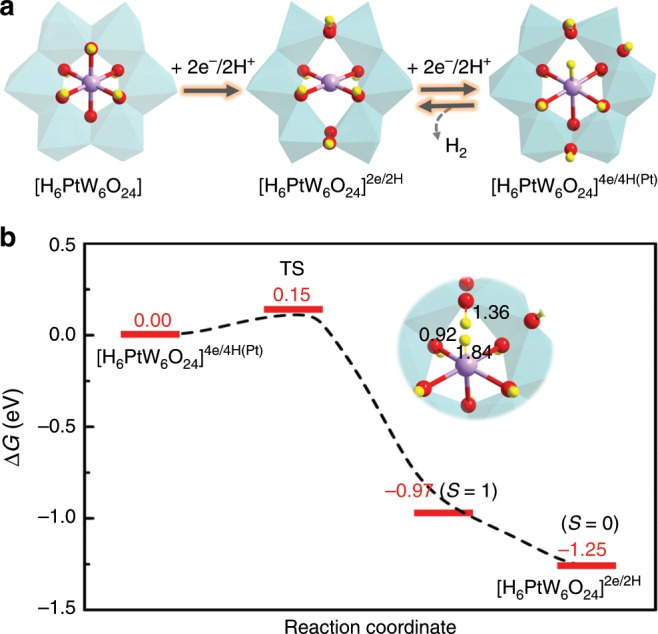
a Mechanistic scheme of the HER catalyzed by PtW6O24/C. [H6PtW6O24] experiences a two-electron/proton-coupled reduction to form [H6PtW6O24]2e/2H (PtII), agreeing well with the intermediate detected by XAS. Two further reductions and intramolecular electronic recombination (Supplementary Fig. 35) were suggested to generate the active [H6PtW6O24]4e/4H(Pt). Catalytic H2 formation is proposed to occur between [H6PtW6O24]2e/2H and [H6PtW6O24]4e/4H. Other pathways are discussed in Supplementary Fig. 35c. b Free energy diagrams for H2 production with an extremely low barrier. H is colored with yellow for clarity.
