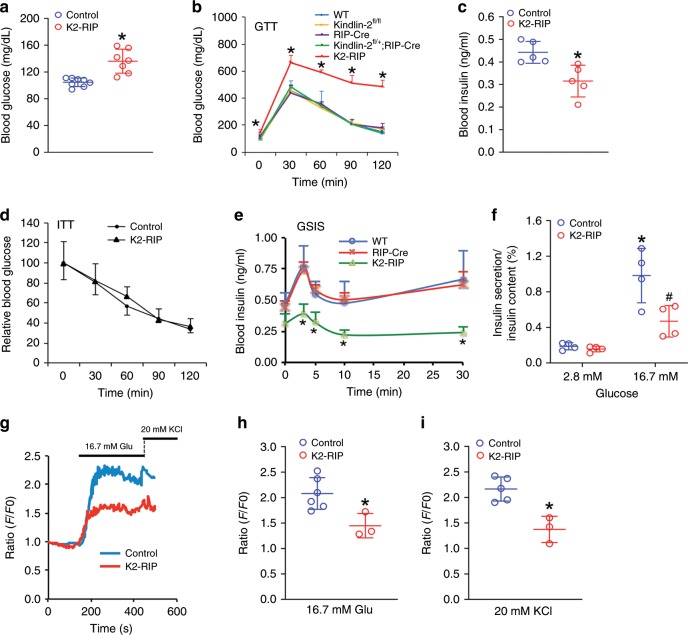
Fig. 2. Kindlin-2 loss causes severe diabetes-like phenotypes without affecting insulin sensitivity.
a Fasting blood glucose level. Two-month-old male control (RIP-Cre) and K2-RIP mice were fasted overnight. *P < 0.05, versus control, N = 8 for control, N = 7 K2-RIP, b GTT. Mice treated as in a were given intraperitoneal injections of glucose (2 g/kg body weight). *P < 0.05, versus control, N = 5 for WT and K2-RIP, N = 6 for Kindlin-2fl/fl, and N = 7 for RIP-Cre and Kindlin-2fl/+; RIP-Cre. c Blood insulin level. Mice were treated as in a. *P < 0.05, versus control, N = 5 mice per genotype. d ITT. Mice fasted (6–7 h) were intraperitoneally injected with a single dose of recombinant human insulin (1 U/kg body weight). *P < 0.05, versus control, N = 6 for control, N = 8 for K2-RIP. e In vivo GSIS. Mice treated as in a and intraperitoneally injected with glucose (2 g/kg body weight). Blood insulin levels were measured by ELISA at 0, 3, 5, 10, and 30 min after glucose injection. *P < 0.05, versus control, N = 5 for WT, N = 8 for RIP-Cre and K2-RIP. f In vitro GSIS. Islets isolated from 2-month-old male control K2-RIP mice were treated with 2.8 or 16.7 mM glucose. Amounts of insulin in supernatant were measured by ELISA assay. Proteins were extracted and total insulin content was measured. Supernatant insulin was normalized to total insulin content. *P < 0.05, versus 2.8 mM glucose, #P < 0.05, versus control. g Ca2+ influx. Representative results from control and K2-RIP islets are provided. N = 15 control islets, N = 20 K2-RIP islets. h Quantification of glucose (16.7 mM) stimulation in control and mutant islets. N = 6 islets for control, N = 3 islets for K2-RIP, *P < 0.05, versus control. i Quantification of KCI (20 mM) stimulation in control and mutant islets. N = 5 islets for control, N = 3 islets for K2-RIP, *P < 0.05, versus control. Results are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (s.d.) and Student’s t test was used in this figure. Source data for a–f, h, i are provided as a Source Data file.