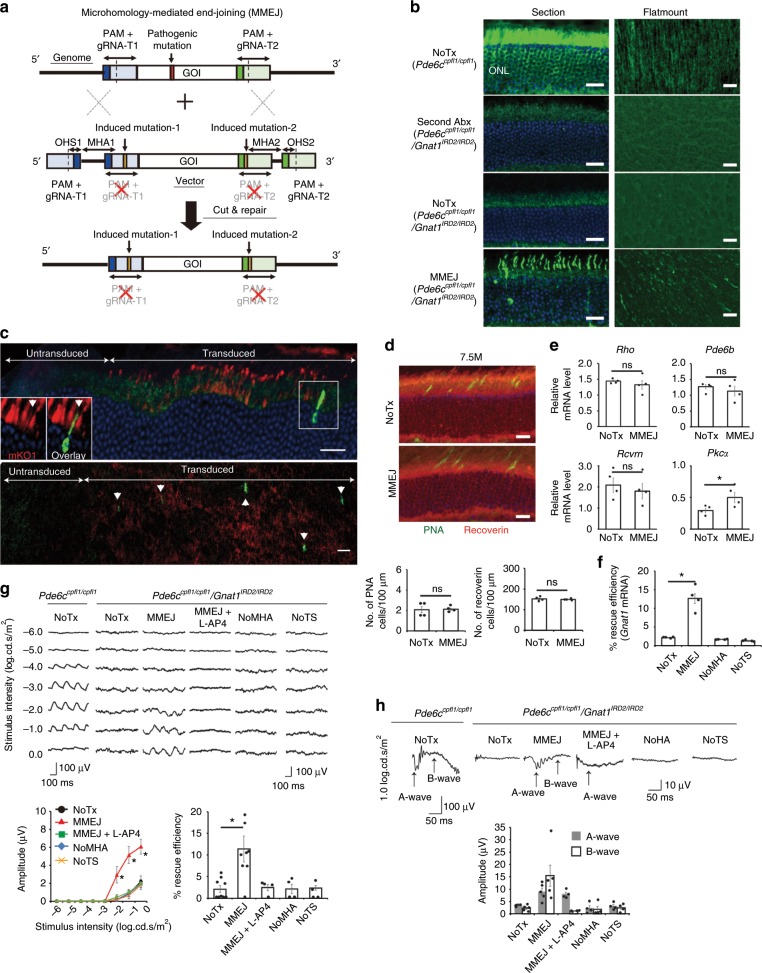
Fig. 1. In vivo characterization of mutation replacement genome editing.
a Illustration of MMEJ-mediated mutation replacement. Genome of interest (GOI) with and without the mutation are excised at the flanking gRNA target sites (gRNA-T1 and -T2; dotted line) from mouse genome and AAV vector, respectively, by SaCas9 and two gRNAs. GOI without mutation is inserted into the genome using microhomology arms (MHA), thereby correcting the mutation. b GNAT1 staining. GNAT1-positive photoreceptors (arrowhead) were observed (section, left; flatmount, right). c Co-localization of Kusabira Orange (mKO1, red) probing SaCas9 expression and GNAT immunopositivity (inset, green). Scattered GNAT-positive cells were observed only in the area transduced with mKO1 (section, top; flatmount, bottom). Note, oversized reporter vector (5201 bp) drastically reduced editing efficiency. N = 4 d PNA and recoverin staining with quantification (N = 4). e RT-PCR of Rho, Pde6b, Rcvrn, and Pkcα (relative to Pde6ccpfl1/cpfl1 mice; N = 4 for all). f Rescue efficiency by RT-PCR of Gnat1 (relative to Pde6ccpfl1/cpfl1 mice; N = 4 for all). g 6-Hz flicker ERGs. N = 9, 9, 4, 4, and 4 for No treatment (NoTx), MMEJ, MMEJ + L-AP4, NoMHA, NoTS, respectively. In MMEJ + L-AP4, MMEJ vector and L-AP4 were sequentially injected. Amplitudes (−1.0 log.cd.s.m−2) relative to those of Pde6ccpfl1/cpfl1 mice indicate %rescue efficiency (bottom right). h. Single flash ERGs. The same group of mice used in g. Scale bar: 20 µm; Data represent mean ± S.E.M.; *P < 0.05 (Student’s t-test); ns, not significant; PAM, protospacer adjacent motif, OHS, over-hanging sequence; Abx, antibodies; NoTS, no gRNA target sites. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.