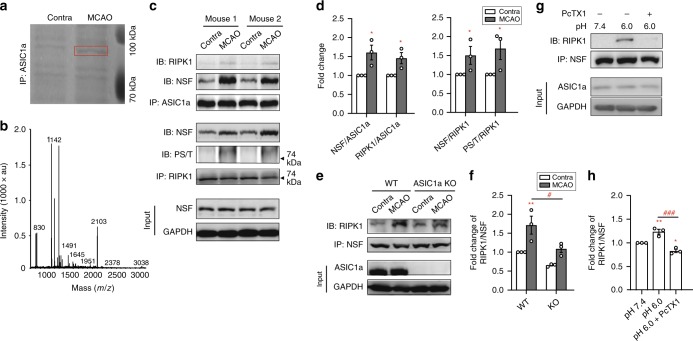
Fig. 3. NSF is recruited to ASIC1a in ischemic brain to form NSF-ASIC1a-RIPK1 complex.
a Image of Coomassie blue staining of SDS-PAGE of immunoprecipitants by a polyclonal ASIC1a antibody from contralateral (Contra) and ischemic (MCAO) hemispheres of a mouse subject to MCAO. Red box indicates the band of interest (~85 kD) reproducibly identified in three independent experiments. b NSF was identified from the ~85 kD band by MALDI-TOF-MS analysis, in which 18 peptide sequences (out of 39) were found to match NSF (GenBank accession no. 18195) with the protein sequence coverage of 22% (Supplementary Data 1). c Confirmation of increased RIPK1-ASIC1a-NSF association in MCAO hemispheres as compared to Contra hemispheres by co-IP. In two examples, both the anti-ASIC1a and anti-RIPK1 antibodies pulled down more NSF from MCAO than Contra groups, along with the markedly increased serine/threonine phosphorylation of RIPK1. Total levels of NSF were not changed after MCAO. d Summary data for (c). n = 3, * p < 0.05 vs. Contra by ANOVA. e Asic1a gene deletion prevented the ischemia-induced increase in RIPK1-NSF association. Anti-NSF antibody pulled down more RIPK1 from MCAO than Contra brain samples from WT but not ASIC1a knockout (KO) mice. f Summary data for (e). n = 3, ** p < 0.01 vs. Contra, # p < 0.05 vs. WT, by ANOVA. g Acidosis (pH 6.0, 1 h) induced RIPK1-NSF association in cultured neurons, which was prevented by pretreatment with PcTX1 (10 nM added at 0.5 h before and maintained during acidosis). h Summary data for (g). n = 3, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, vs. pH 7.4, ### p < 0.05 vs. pH 6.0, by ANOVA. Error bars are SEM for all summary panels.